A Comprehensive Analysis of Plastic Versus Metal Materials in Car Fuse Holders for Durability and Performance
News 2025-10-20
Car fuse holders are critical components in automotive electrical systems, protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits. The choice of material—plastic or metal—significantly impacts durability, safety, and overall performance. This article compares plastic and metal options, focusing on their ability to withstand environmental stresses, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical wear in various driving conditions. Understanding these materials helps in selecting the right fuse holder for specific automotive applications, ensuring reliability and longevity.
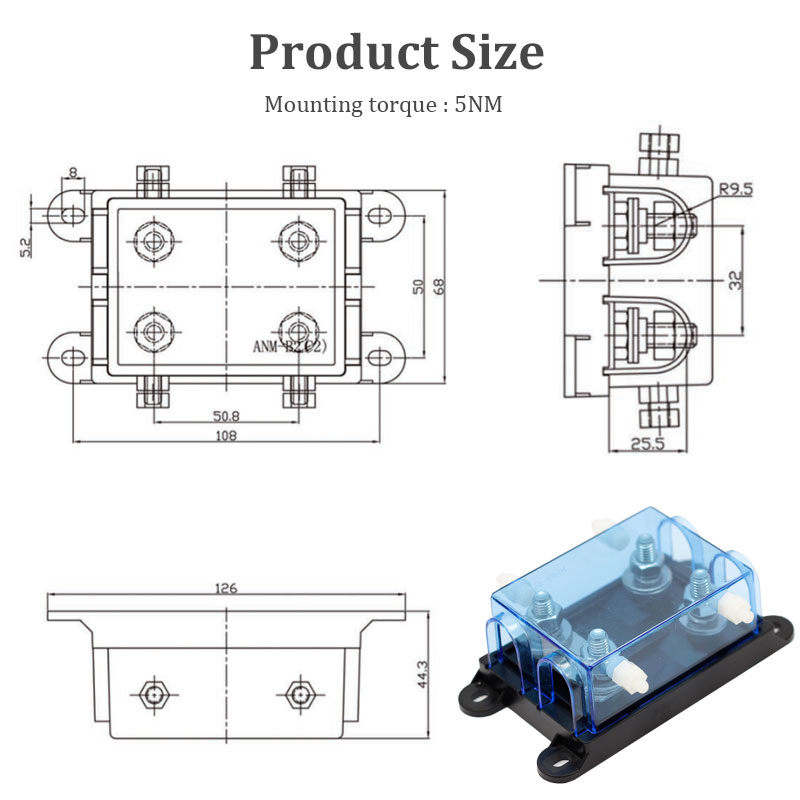
Advantages and Limitations of Plastic Fuse Holders
Plastic fuse holders offer several benefits in automotive use, primarily due to their lightweight nature and electrical insulation properties. They are cost-effective to produce, making them ideal for mass-market vehicles where budget constraints are key. In terms of durability, plastics like nylon or polycarbonate resist corrosion and chemicals better than some metals, performing well in humid or wet environments. However, they can degrade under high heat or UV exposure, leading to cracking or deformation over time. This makes plastic holders suitable for standard passenger cars but less ideal for high-performance or off-road applications where extreme conditions are common.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Metal Fuse Holders
Metal fuse holders, often made from aluminum or steel alloys, excel in scenarios demanding superior mechanical strength and heat dissipation. Their robustness allows them to handle vibrations and impacts better, reducing the risk of failure in rugged terrains or heavy-duty vehicles. Metals conduct heat efficiently, which can prevent overheating in high-current situations, enhancing safety. On the downside, they are prone to corrosion if not properly coated, and their weight can add unnecessary bulk to the vehicle’s design. This material is preferred in industrial or commercial fleets but may increase costs and complexity in everyday automotive setups.
Application Scenarios and Performance Comparison
In automotive contexts, material choice depends on specific use cases and performance needs. Plastic holders shine in compact, fuel-efficient cars where space and weight savings are prioritized, offering good insulation and ease of installation. Metal variants provide enhanced durability in demanding environments, such as electric vehicles or those exposed to harsh weather, with better resistance to thermal cycling and physical stress. Comparing the two, metals generally outperform plastics in longevity under extreme conditions, but plastics offer cost and versatility advantages for routine applications. Selecting the appropriate material ensures optimal fuse holder performance, balancing factors like cost, weight, and environmental resilience for improved vehicle reliability.


