A Detailed Breakdown of Expenses for Automotive Fuse Substitutions: OEM Reliability Versus Budget-Friendly Aftermarket Choices
News 2025-10-13
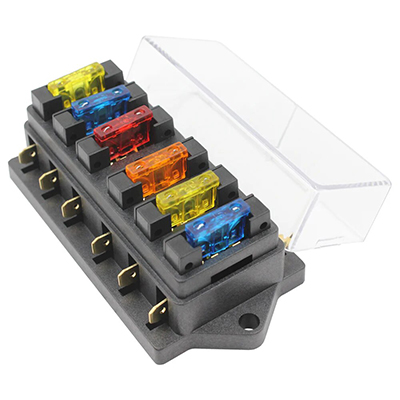
Car fuses are essential components in any vehicle’s electrical system, acting as safeguards against overloads and short circuits. When a fuse blows, it prevents damage to wiring and other parts, but replacement costs can vary widely. This article explores the financial aspects of replacing car fuses, comparing original equipment manufacturer (OEM) options with aftermarket alternatives. Understanding these costs helps drivers make informed decisions, balancing quality and budget in maintenance routines. Fuses are commonly found in applications like lighting, audio systems, and engine controls, where reliability is key to safe operation.
Common Applications and Scenarios for Fuse Replacement
Car fuses serve critical roles in various vehicle systems, such as protecting the battery, ignition, and accessory circuits. In everyday scenarios, fuses often blow due to minor issues like a faulty light bulb or a power surge from extreme weather. For instance, in modern cars with advanced electronics, fuses in the infotainment system or ADAS components must handle higher currents, demanding precise replacements. OEM fuses are designed for specific models, ensuring optimal performance in high-stress environments, while aftermarket options provide versatility for older vehicles or custom setups. This makes fuse selection crucial for maintaining electrical integrity and avoiding recurrent failures.
Performance Advantages of OEM and Aftermarket Fuses
OEM fuses offer superior compatibility and durability, engineered to match the exact specifications of your vehicle’s make and model, which enhances long-term reliability. They excel in performance-critical applications, such as engine management systems, where precise current ratings prevent false trips or failures. Aftermarket fuses, on the other hand, provide cost savings and wider availability, often with similar materials and ratings, making them ideal for routine maintenance in less demanding scenarios. While OEM options might cost $5 to $15 per fuse, aftermarket ones range from $1 to $5, offering better value for budget-conscious drivers without compromising essential safety features.
Frequently Asked Questions on Fuse Replacement
1. What factors influence the cost of replacing a car fuse?
Answer: Costs depend on the fuse type, vehicle model, and whether you choose OEM or aftermarket parts; labor fees from a mechanic can add $50 to $100 if professional installation is needed.
2. How can I identify if a fuse needs replacement?
Answer: Look for signs like electrical malfunctions, such as non-working lights or dashboard warnings; use a multimeter to test continuity or visually inspect for a broken filament.
3. Are there benefits to using aftermarket fuses over OEM?
Answer: Aftermarket fuses are often cheaper and readily available, providing good performance for standard applications, but they may not match the exact specifications, potentially affecting longevity in high-demand systems.