A Detailed Examination of Auto Fuse Size Options and Their Compatibility with Standard Car Electrical Panels
News 2025-10-24
Auto fuses are critical components in vehicle electrical systems, protecting circuits from overloads and short circuits. Proper selection of fuse sizes ensures safety and reliability in automotive applications. This article explores the various fuse size options available and how they align with standard car electrical panels, focusing on practical compatibility and performance benefits.
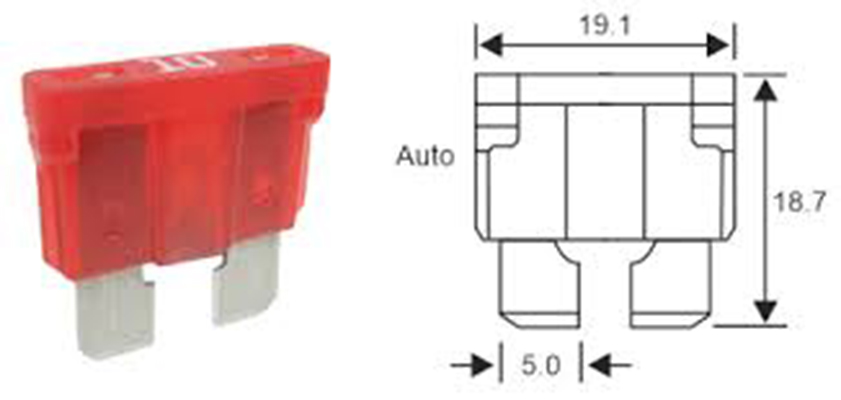
Common Auto Fuse Sizes
Standard auto fuse sizes typically range from 5A to 30A, with common types including blade, glass, and ceramic fuses. These sizes correspond to the amperage ratings needed for different circuits, such as lighting, audio systems, or engine controls. For instance, a 10A fuse might protect interior lights, while a 20A fuse could handle power windows. Selecting the right size involves understanding the circuit’s maximum current draw to avoid failures or hazards.
Ensuring Compatibility with Electrical Panels
Compatibility between fuse sizes and car electrical panels depends on factors like voltage ratings and physical dimensions. Standard panels often feature slots designed for specific fuse types, ensuring a secure fit and proper operation. In application scenarios, such as upgrading a car’s audio system, choosing compatible fuses prevents issues like melting or poor contact. Performance advantages include enhanced circuit protection and longevity, as the correct size reduces the risk of nuisance blowing or inadequate safeguarding against faults.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the standard auto fuse sizes available?
Common sizes include 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, and 30A, catering to various electrical loads in vehicles.
2. How do fuse sizes match with car electrical panels?
Fuse sizes align with panel slots based on amperage and type, ensuring safe current flow and protection for specific circuits.
3. What benefits come from correct fuse size selection?
Proper sizing enhances safety by preventing overloads, improves system efficiency, and extends the lifespan of electrical components.


