An In-Depth Examination of Automotive Fuse Types: Covering Blade, Cartridge, and Glass Variants and Their Applications in Vehicles
News 2025-10-24
Automotive fuses are critical components in vehicle electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overcurrent and short circuits. These fuses act as safeguards, preventing damage to wiring and electronic components by breaking the circuit when excessive current flows. Among the various types, blade, cartridge, and glass fuses stand out due to their widespread use in cars, trucks, and other vehicles. Each type offers unique characteristics suited to different applications, ensuring reliable performance in diverse automotive environments. Understanding these fuse variants helps in selecting the right one for specific needs, enhancing vehicle safety and longevity.

Blade Fuses
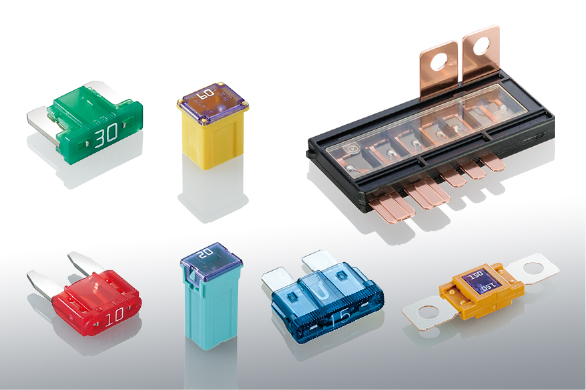
Blade fuses, also known as spade or plug-in fuses, feature a flat, blade-like design that allows for easy insertion and removal. They are commonly used in modern vehicles for protecting low-voltage circuits such as lighting, audio systems, and power windows. In application scenarios, blade fuses excel in compact spaces due to their small size and color-coded ampere ratings, which simplify identification and replacement. Performance advantages include quick response times to overcurrent events, high reliability in automotive vibrations, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for everyday vehicle maintenance and upgrades.
Cartridge Fuses
Cartridge fuses consist of a cylindrical body with metal end caps, housing a fuse element that melts under high current. They are often employed in heavier-duty applications, such as in trucks or industrial vehicles, where higher current capacities are required for systems like engine controls and heating elements. For instance, cartridge fuses are preferred in scenarios involving robust environmental conditions, providing strong protection against short circuits. Their performance benefits include superior breaking capacity, resistance to temperature fluctuations, and longer lifespan compared to other types, ensuring consistent safeguarding of critical automotive circuits under demanding conditions.
Glass Fuses
Glass fuses feature a transparent glass tube enclosing a thin wire filament, allowing visual inspection to check if the fuse has blown. They are typically found in older vehicles or specific low-current applications, such as dashboard instruments and accessory circuits, where space constraints are less of an issue. In practical use, glass fuses are valued for their ability to handle precise current ratings in sensitive electronics. Key performance advantages include easy fault detection through visibility, accurate response to overcurrent, and suitability for environments where quick visual checks are beneficial, contributing to efficient troubleshooting and maintenance in automotive settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the primary functions of auto fuses?
They protect vehicle electrical systems by interrupting current flow during faults, preventing damage to wires and components.
2. How do blade and glass fuses differ in design?
Blade fuses have a flat, plug-in design for easy access, while glass fuses use a transparent tube for visual inspection of the element.
3. Why choose cartridge fuses for certain vehicles?
Cartridge fuses offer higher current handling and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications in trucks and machinery.