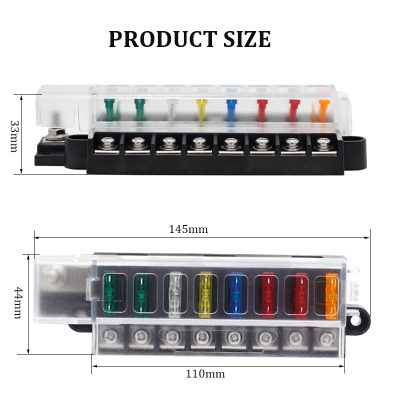
Battery fuse technology that protects vehicle batteries against reverse polarity and high‑energy surges
News 2025-11-17
Battery fuse protects vehicle battery from reverse polarity and surges
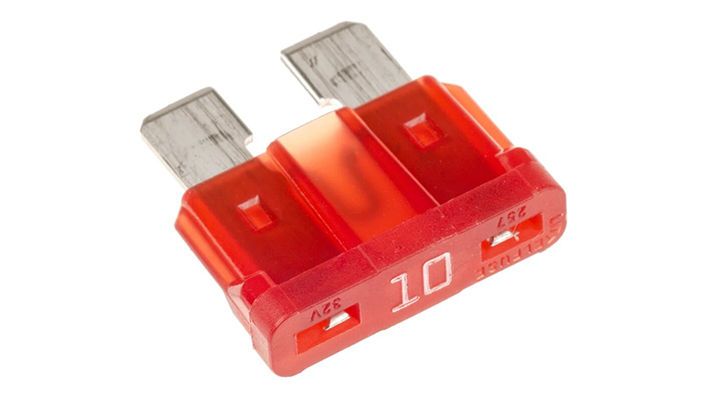

Role of the Battery Fuse in Modern Vehicle Platforms
A battery fuse is a safety component placed close to the vehicle battery to interrupt current when abnormal conditions occur. In modern 12 V, 24 V, and emerging 48 V architectures, this fuse protects wiring harnesses, ECUs, and the battery itself against reverse polarity connection, accidental short circuits, and high surge currents during fault events. By opening the circuit in milliseconds, the fuse prevents overheating of cables and terminal lugs, reduces fire risk, and limits mechanical damage to cells. Automakers now treat the battery fuse as a core part of the power distribution network rather than a low-level accessory.
Protection from Reverse Polarity and Installation Errors
Reverse polarity events often happen during maintenance, jump starting, or aftermarket installation of audio amplifiers, winches, and DC‑DC converters. When terminals are accidentally swapped, sensitive electronics can be destroyed within microseconds. A properly selected battery fuse, coordinated with reverse polarity protection circuitry, acts as a sacrificial element that opens before ECUs, sensors, and semiconductor switches are exposed to damaging current. High breaking‑capacity designs handle the instantaneous inrush that occurs when a reversed connection is made, avoiding catastrophic arc formation at the battery posts.
Surge Performance, Breaking Capacity, and Design Advantages
Battery fuses for automotive use are engineered to withstand harsh thermal cycles, vibration, and surge loads caused by start‑stop systems, regenerative braking, and inductive accessories. Key specifications include rated voltage, continuous current, I²t value, and maximum interrupt rating. High interrupt capacities up to several kiloamps allow safe clearing of short circuits near the battery, while low internal resistance minimizes power loss and voltage drop in normal operation. Compact blade or bolt‑down packages simplify integration into battery junction boxes and meet stringent OEM standards such as ISO 8820 and LV 124, supporting long service life and predictable time‑current characteristics.
Application Scenarios in ICE, Hybrid, and EV Platforms
Battery fuses see wide deployment across internal combustion vehicles, mild hybrids, full hybrids, and battery electric vehicles. In conventional passenger cars they protect starter circuits, body control modules, and comfort systems such as HVAC and infotainment. Off‑road equipment, trucks, and buses use higher‑rating fuses to safeguard heavy‑duty alternators, hydraulic pumps, and auxiliary power outputs. In EVs and plug‑in hybrids, specialized fuses support 48 V subsystems, high‑capacity lithium packs, and on‑board chargers, working alongside contactors and current sensors to contain short circuits, manage fault energy, and maintain functional safety compliance according to ISO 26262.
Installation Best Practices and Maintenance Considerations
Engineers should position the battery fuse as close as possible to the positive terminal, reduce cable length between battery and fuse, and use properly rated conductors. Correct torque on bolt‑down versions maintains low contact resistance, cutting the risk of local heating and nuisance openings. During service, technicians must replace opened fuses only with parts matching original rating, voltage class, and automotive approval, while checking the underlying cause of the fault. Visual inspection of discoloration, cracking, or loose hardware helps identify early degradation, keeping power distribution secure throughout the vehicle lifetime.
1Key question: Why is a battery fuse vital in reverse polarity events?
The fuse interrupts extremely high fault current before it reaches electronic control units, protecting semiconductors and wiring from permanent damage caused by accidental terminal reversal.
2How does surge performance affect real vehicle applications?
Strong surge performance and high interrupt rating allow the fuse to safely handle starter inrush, inductive loads, and short circuits, improving overall safety and system uptime.
3What should designers consider when selecting an automotive battery fuse?
Designers must evaluate system voltage, continuous load, peak fault current, ambient temperature, mounting style, and automotive qualification to ensure coordination with cables and downstream protection devices.