Efficient Thermal Fuse Technology Enhances Automotive Electrical Fire Protection
News 2025-11-27
Efficient thermal fuses play a decisive role in modern vehicle safety by interrupting electrical current when abnormal heat is detected. As automotive platforms integrate high-power infotainment, electric drive systems, and dense wiring harnesses, the risk of localized overheating increases. A properly selected thermal fuse responds to excessive temperature before insulation fails or components ignite, creating a passive layer of protection that does not depend on software or user intervention.
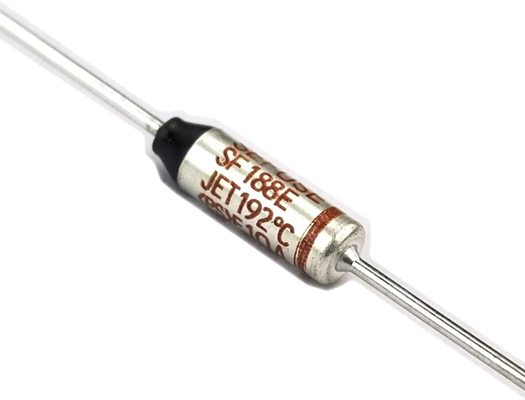

Key Operating Principle and Safety Mechanism
A thermal fuse contains a temperature-sensitive element engineered to open the circuit permanently when a preset threshold is exceeded. Unlike resettable devices, it provides a one-time, definitive interruption that prevents current from flowing through a compromised circuit. This operating principle is particularly valuable in sealed or hard-to-access automotive environments where maintenance may be infrequent. Once activated, the open circuit halts further heat buildup, helping prevent wire harness damage, connector melting, and potential fire in crowded engine bays and cabin modules.
Performance Advantages in Automotive Applications
Modern thermal fuses offer tight temperature tolerances, fast response, and low resistance, ensuring minimal power loss during normal operation. Compact axial or radial packages fit into dense wiring harnesses, motor windings, battery packs, and LED lighting modules. Their predictable blowing temperature allows engineers to coordinate thermal protection with other components such as PTCs and circuit breakers. High interrupt ratings enable the fuse to safely disconnect even under substantial fault currents commonly present in 12 V, 24 V, and high-voltage EV architectures, enhancing overall system safety while keeping design complexity under control.
Typical Use Cases in Vehicle Systems
Thermal fuses are widely used in seat heaters, HVAC blowers, window defoggers, fuel pump modules, and on-board chargers. In seat heating mats, a fuse reacts when a localized hotspot forms due to mechanical damage or prolonged overcurrent, preventing upholstery ignition. Within electric power steering and cooling fan assemblies, the device protects motor windings from thermal runaway during blocked rotor conditions. In high-voltage battery packs and DC-DC converters, carefully positioned thermal fuses act as a last line of defense, complementing electronic monitoring by disconnecting sections that exceed safe temperature limits.
Selection, Integration, and Reliability Considerations
Selecting an appropriate thermal fuse requires evaluation of nominal operating temperature, ambient profile, maximum fault current, and expected lifetime. Designers must ensure good thermal coupling between the fuse body and the protected hotspot, often using sleeves, clips, or direct contact mounting. Automotive-grade devices undergo rigorous vibration, humidity, and thermal cycling tests to guarantee long-term stability. Proper integration in compliance with ISO and OEM standards supports high safety ratings and helps manufacturers meet regulatory requirements related to fire risk reduction in passenger and commercial vehicles.
Questions and Answers
1How does a thermal fuse differ from a standard current fuse?
A thermal fuse responds primarily to temperature rather than overcurrent, opening the circuit when its rated temperature is reached, even if current remains within nominal limits.
2Where is a thermal fuse typically installed in a vehicle?
It is commonly installed in seat heaters, blower motors, battery modules, lighting systems, and other areas where excessive heat can occur but may not be immediately visible.
3Can a thermal fuse be reset after activation?
No, a thermal fuse is a non-resettable device; once it opens due to excessive temperature, it must be replaced to restore circuit continuity.