Heavy-Duty-Performance Thermal Fuse Enables High-Power Vehicle Electronics Protection
News 2025-11-27
High-power on-board electronics in modern vehicles demand precise and durable protection solutions. The heavy-duty-performance thermal fuse has emerged as a key safeguard for traction inverters, on-board chargers, DC/DC converters, and high-capacity battery packs. By reacting accurately to abnormal temperature rise, it interrupts current before damage propagates through wiring harnesses, control modules, or energy storage systems. This component supports higher continuous loads and aggressive transient conditions without compromising safety, making it suitable for new-generation electric, hybrid, and intelligent commercial vehicles.
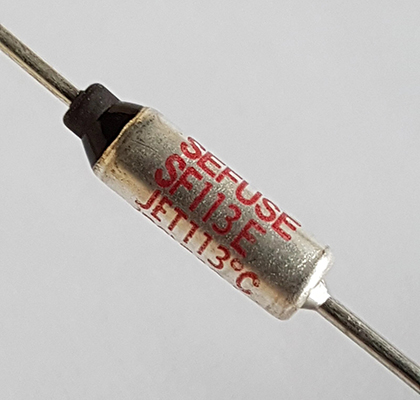

Core Design Features and Performance Advantages
The heavy-duty thermal fuse is engineered around a temperature-sensitive alloy pellet or organic element that melts at a precisely calibrated trip point. Its internal structure uses low-resistance contact materials to handle elevated current levels found in powertrain and fast-charging applications. Key performance benefits include tight opening temperature tolerance, high breaking capacity, and low leakage under normal conditions. These characteristics minimize power loss, reduce heat buildup, and maintain stable operation in dense electronic architectures. The design also controls arc formation during interruption, protecting adjacent components and connectors.
High-Power Vehicle Application Scenarios
In battery-electric and plug-in hybrid platforms, the thermal fuse plays an important role in secondary protection alongside fuses and circuit breakers. It is commonly installed in battery junction boxes, heater modules, high-current harness segments, and power distribution units operating under harsh thermal cycles. When cooling system anomalies or connector faults create local hotspots, the fuse responds at the defined threshold, isolating the affected branch. Heavy-duty capability allows integration into 48 V mild hybrid systems, electric power steering, air-conditioning compressors, and high-power infotainment amplifiers, where conventional fuses may not withstand elevated load durations.
Integration, Standards Compliance, and Lifetime
For automotive designers, compatibility with manufacturing and safety standards is crucial. The heavy-duty thermal fuse is typically available in radial, axial, or surface-mount packages tailored to automated assembly lines and compact PCB layouts. Products are tested to automotive-grade vibration, humidity, and thermal shock requirements, ensuring stable characteristics throughout vehicle life. Proper thermal coupling to heat sources, along with correct orientation and derating, helps maintain predictable activation. When selected and placed according to system design rules, the fuse contributes to meeting ISO 26262 functional safety targets and supports high MTBF values in complex electronic control units.
Selection Guidelines and System-Level Benefits
Selecting the appropriate heavy-duty-performance thermal fuse involves defining rated current, opening temperature, maximum voltage, and interruption capability under worst-case fault conditions. Engineers evaluate thermal profiles of PCBs, cable assemblies, and power modules to choose trip points that protect both semiconductor devices and insulation materials. This approach enables higher power density, extended operating ranges, and improved user safety in passenger cars, buses, and industrial vehicles. The resulting system gains include reduced risk of thermal runaway, simplified layout compared to more complex active protection schemes, and improved compliance in high-power charging infrastructures.
1、How does a heavy-duty thermal fuse differ from a standard fuse?
A heavy-duty thermal fuse reacts primarily to temperature rather than only overcurrent, manages higher power levels, and offers tighter thermal activation tolerances suited to vehicle electronics.
2、Where is this thermal fuse typically installed in vehicles?
It is widely used in battery packs, power distribution units, inverters, DC/DC converters, heater modules, and high-current harness sections exposed to demanding thermal conditions.
3、What criteria matter most during component selection?
Key criteria include rated current, opening temperature range, voltage rating, breaking capacity, environmental robustness, and mechanical format compatibility with the target assembly.