Non-Corrosive-Material Thermal Fuse Sustains Performance In Harsh Industrial Conditions
News 2025-11-27
Non-corrosive-material thermal fuses are becoming a key safety component in demanding electrical and electronic systems where conventional fuses degrade too quickly. By employing corrosion-resistant alloys, engineered encapsulation, and moisture-tolerant terminations, this class of thermal fuse maintains accurate opening temperatures and low contact resistance over a long service life. Designers in automotive electronics, industrial automation, renewable energy conversion, and outdoor power equipment increasingly adopt these devices to preserve system safety even under vibration, temperature shock, and chemical exposure.
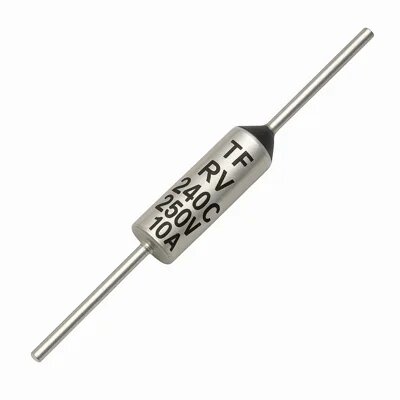

Construction Features And Core Performance Advantages
Non-corrosive-material thermal fuses use specially selected metals and plating that resist oxidation, sulfurization, and galvanic attack. Stable eutectic pellets or organic charge materials are paired with robust lead-wires and a sealed housing, minimizing drift of the rated cutoff temperature. This structure delivers consistent fusing behavior after thousands of heating and cooling cycles, avoiding nuisance trips and late action. Low internal resistance supports efficient current flow, reducing self-heating and power loss. Compliance with UL, VDE, and RoHS requirements ensures the device can be integrated into safety-certified assemblies across global markets.
Performance In Harsh And Contaminated Environments
In harsh conditions, corrosion often initiates at contact surfaces, gradually increasing resistance and changing the actual opening temperature of conventional thermal links. Non-corrosive versions counter this failure mode through nickel- or silver-based alloys, protective passivation layers, and high-quality glass or resin sealing. They remain stable in environments featuring salt spray, oil mist, condensate, and flux residues. Long-term tests under high humidity, elevated temperature storage, and mixed gas exposure demonstrate minimal shift in calibration. This consistent performance gives engineers confidence to deploy them in sealed motor assemblies, battery packs, and outdoor enclosures where maintenance access is limited.
Application Scenarios Across Key Industry Segments
Typical applications include overtemperature protection in EV battery modules, on-board chargers, and DC/DC converters exposed to road salt and vibration. In industrial drives, thermal fuses are embedded near power IGBTs or MOSFETs to prevent thermal runaway when fans fail or cooling channels clog. LED street lighting power supplies and telecom base station equipment use non-corrosive fuses to ensure stable operation under wide climatic variations and air pollution. Household appliances such as coffee machines, clothes dryers, and induction cookers benefit from long-term stable cutoff in steam-rich and detergent-contaminated environments, reducing warranty returns and service costs.
Design Considerations And Selection Recommendations
Engineers should first define the maximum allowable temperature of the protected component and select a fuse rated just below this limit, accounting for tolerance, mounting method, and ambient rise. Current rating must exceed the normal operating current with adequate margin for inrush. When targeting harsh environments, preference should be given to fuses featuring sealed construction, corrosion-resistant leads, and proven performance data under humidity and mixed gas tests. Proper thermal coupling using clips, crimp sleeves, or thermally conductive adhesives ensures fast and accurate response. Validation under worst-case load profiles, including locked-rotor, blocked airflow, and abnormal charging states, helps confirm safe operation over the product lifetime.
1. What distinguishes a non-corrosive thermal fuse from standard types?
Non-corrosive thermal fuses use corrosion-resistant materials and sealed structures that maintain their rated opening temperature and low contact resistance even in humid or chemically aggressive environments.
2. Where are non-corrosive thermal fuses most commonly used?
They are widely applied in EV battery systems, industrial motor drives, outdoor LED drivers, telecom power units, and high-end household appliances operating under moisture, dust, or chemical exposure.
3. How should engineers choose the correct non-corrosive thermal fuse?
Selection should consider cutoff temperature, current rating, environmental conditions, mounting method, and certification requirements, supported by manufacturer reliability data under harsh-condition testing.