Precision-Engineered Thermal Fuse Solution Enhancing Safe Power Control In Modern Vehicles
News 2025-11-27
Precision-engineered thermal fuses are becoming a key safety component in next-generation automotive electrical systems. As vehicles integrate high-density electronics such as advanced driver assistance modules, infotainment platforms, battery management units, and high-power LED lighting, the risk of localized overheating and circuit overload grows. A dedicated thermal fuse interrupts the circuit once a preset temperature is reached, providing a passive, fail-safe protection layer that supports both passenger safety and long-term component reliability.
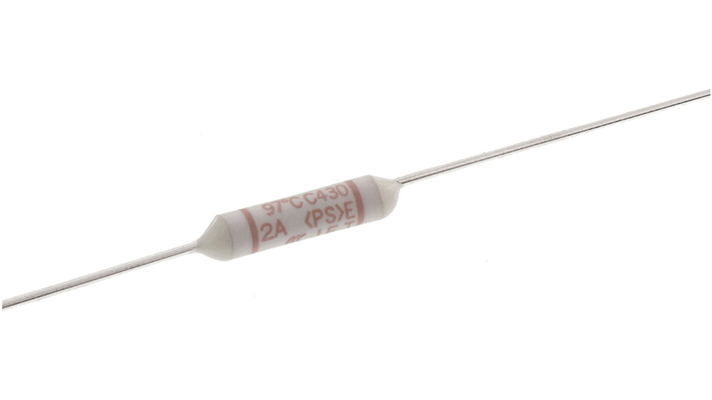
Core Operating Principle And Construction
The thermal fuse used in vehicle assemblies is typically a non-resettable, one-shot device designed around a calibrated fusible alloy or pellet. Under normal operating conditions, current flows through the fuse with minimal resistance and negligible power loss. When abnormal heat builds up due to overload, short circuit, blocked airflow, or mechanical failure, the internal element reaches its melting or deformation point. This triggers permanent opening of the circuit, preventing further temperature rise. Precision engineering of the melting alloy, contact spring, and encapsulation materials ensures a narrow tolerance band between normal peak temperature and trip temperature, avoiding nuisance opening while still reacting quickly to genuine fault conditions.
Key Performance Advantages In Automotive Applications
Automotive-grade thermal fuses are specified to withstand wide ambient ranges, continual vibration, and humidity typically encountered in engine bays, under-seat modules, and trunk-mounted electronic units. Low internal resistance and optimized contact plating minimize self-heating, supporting accurate thermal sensing of the surrounding component or PCB area. The calibrated trip temperature can be selected to match the maximum allowable temperature of nearby semiconductors, coils, or plastic housings. High breaking capacity ratings enable the fuse to safely interrupt fault currents in 12 V and 48 V electrical architectures without arcing damage. The result is stable, maintenance-free protection over the entire service life of the vehicle.
Typical Use Cases In Vehicle Electrical And Electronic Systems
Thermal fuses are widely integrated into heater elements in seat warmers, steering wheel heaters, mirror defoggers, and cabin air blowers, protecting occupants from burns as well as avoiding damage to upholstery and trim. They are also embedded in DC motors, power window drives, fuel pumps, and cooling fans, where rotor lock or mechanical obstruction can rapidly raise winding temperature. In power electronics, a thermal fuse may be placed in battery junction boxes, onboard chargers, DC-DC converters, and LED driver modules, acting as the last line of defense if thermal management or electronic current limiting fails. Compact radial or axial packages allow direct placement on busbars or heat-sensitive PCB zones, improving reaction speed and reducing wiring complexity.
Selection, Integration, And Compliance Considerations
Choosing the correct thermal fuse for an automotive project requires alignment of trip temperature, rated current, and voltage with the real operating profile of the circuit. Engineers typically analyze worst-case load, hotspot mapping, and airflow inside enclosures to locate the most thermally representative mounting point. Proper mechanical coupling using clips or thermal adhesives ensures fast heat transfer from the protected component to the fuse body. For compliance, high-quality thermal fuses support standards such as UL, IEC, and automotive-specific requirements such as AEC-Q200 qualification, endurance testing under temperature cycling, and vibration testing. Traceable manufacturing and lot testing help OEMs maintain consistent performance across global vehicle platforms.
Practical Questions And Answers
1How does a thermal fuse differ from a standard electrical fuse?
A thermal fuse reacts primarily to temperature, not just current, opening the circuit when a defined temperature threshold is exceeded, even if current stays within nominal range.
2Where should a thermal fuse be placed in a vehicle module?
It should be mounted as close as possible to the expected hotspot, such as heater elements, motor windings, or power semiconductors, using good thermal coupling so it accurately tracks local temperature.
3Can a blown thermal fuse be reset or reused?
No. It is a non-resettable safety device; once it opens, the component must be replaced to restore protection and ensure continued compliance with safety standards.