Safety-Focused Thermal Fuse Minimizes Electrical Hazards in Modern Vehicle Power Networks
News 2025-11-27
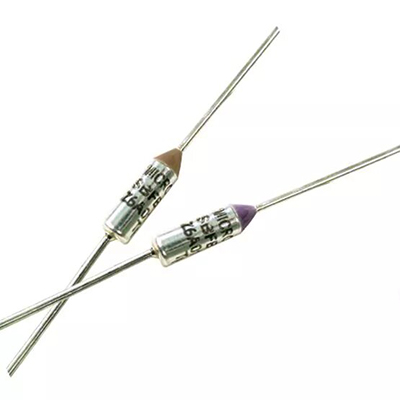
Thermal fuses dedicated to safety management are becoming a decisive element in modern vehicle electrical systems. As onboard power networks grow more complex, high-density wiring, compact control modules, and powerful battery architectures increase the risk of overheating and short circuits. A safety-focused thermal fuse provides a one-time, irreversible cutoff when abnormal temperature rises occur, preventing cable insulation damage, connector melting, and potential fire. By pairing precise opening characteristics with automotive-grade robustness, this component supports higher power levels while maintaining strict functional safety targets.

Key Role In Vehicle Electrical Architecture
Thermal fuses are deployed in battery junction boxes, on-board chargers, DC/DC converters, seat heating modules, HVAC blowers, lighting controllers, and infotainment units. In these locations they act as a final protective barrier, disconnecting the circuit if other control strategies fail or lose power. The fuse element melts at a calibrated temperature triggered by prolonged overloads, blocked ventilation, mechanical faults, or component aging. Once activated, the circuit remains safely open, allowing service personnel to locate the root cause instead of facing intermittent or hidden failures.
Performance Advantages And Safety Compliance
Compared with conventional fuses that only react to current, a thermal fuse responds directly to temperature at the hotspot, which suits tightly packed electronic assemblies. Devices optimized for automotive use feature narrow trip tolerances, low thermal resistance, and stable behavior across wide ambient ranges from engine bay to cabin interior. High interrupt ratings and certified insulation performance allow their use in high-voltage hybrid and battery-electric platforms. Compliance with AEC-Q standards and alignment to ISO 26262 safety concepts help OEMs document quantitative safety goals and reduce system-level risk indices.
Application Scenarios In Electric And Hybrid Vehicles
In traction battery packs, thermal fuses can be integrated into sensor harnesses, cell supervision circuits, and auxiliary heater lines, where localized hotspots may develop faster than current thresholds indicate. DC/DC converters benefit from thermal cutoff on the primary and secondary sides to protect magnetics, MOSFETs, and control boards against cooling failures or clogged filters. Cabin comfort features such as steering wheel heaters, seat heaters, and PTC heaters use thermal fuses to prevent surface temperatures from exceeding safety limits, preserving trim materials and passenger safety. Compact LED driver modules in headlamps and rear lamps also adopt thermal fuses to guard optics and housings under extreme ambient heat.
Design Considerations And Integration Practices
Selecting the correct thermal fuse rating requires careful analysis of normal operating temperature, transient peaks, and worst-case thermal stacking in confined spaces. Engineers mount the fuse in direct contact with suspected hotspots, using clips or welded connections that minimize additional thermal resistance. Layout decisions consider creepage and clearance, mechanical vibration, and service accessibility. System-level simulations combine ambient profiles, duty cycles, and fault scenarios to validate that the opening temperature is high enough to avoid nuisance trips, yet low enough to prevent insulation breakdown. By capturing these parameters early in the design phase, development teams shorten validation cycles and reduce countermeasure costs.
1、How does a thermal fuse differ from a resettable protector?
A thermal fuse opens once and must be replaced, which guarantees permanent isolation after a severe overtemperature event, unlike resettable devices that may reconnect into an unsafe condition.
2、Where is a safety-focused thermal fuse most valuable in vehicles?
It is especially valuable in battery systems, DC/DC converters, and heating circuits where localized hotspots can escalate quickly and pose fire hazards.
3、What factors influence the choice of opening temperature?
Engineers consider normal operating range, maximum allowable component temperature, expected ambient conditions, and regulatory safety margins when specifying the opening point.