Selecting the Ideal Inline Fuse Holder Based on Current Rating and Size Specifications
News 2026-01-12
Inline fuse holders serve as essential elements in electrical systems, housing fuses that interrupt current flow under overload or fault conditions. These components find use in automotive wiring, marine electronics, and industrial control panels. Selecting the right holder requires evaluating amp rating, conductor gauge compatibility, and environmental limits to guarantee safe performance. This overview introduces key considerations for matching fuse holders to application needs.
Understanding Fuse Holder Amp Ratings
The amp rating of an inline fuse holder defines the highest continuous current it can handle before the fuse activates. Operating beyond this rating may cause overheating or unpredictable performance. Engineers should compare nominal circuit current and transient spikes against fuse specifications. Choosing a holder rated modestly above normal load current minimizes false trips while maintaining robust overcurrent protection. Industrial designers rely on accurate rating margins to accommodate intermittent loads in HVAC controls or battery management systems.
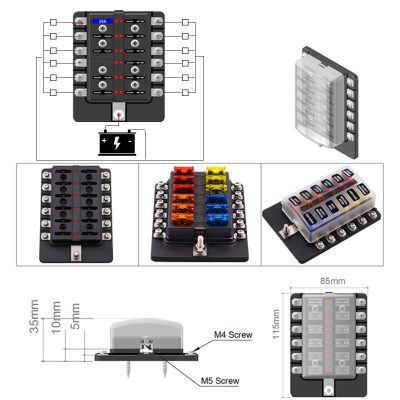
Assessing Physical Dimensions and Connection Types
Inline fuse holders come in various form factors—blade, glass tube, and cartridge styles—each matching specific fuse types and panel layouts. Competent selection involves matching holder body dimensions to panel cutouts and verifying terminal or wire-end connectors such as solder tabs, quick disconnects, or in-line clamps. Proper fitment reduces vibration-induced failures and simplifies service access. When panel space is limited, low-profile holders offer compact integration while maintaining accessibility. Color-coded housings further aid rapid identification.
Installation Scenarios and Performance Benefits
Installation environments determine material choices: UV-resistant plastics suit outdoor or marine applications, whereas high-temperature polymers serve engine compartments. A sealed, watertight holder prevents moisture ingress in harsh settings. Strategically placing fuse holders near charging systems or critical loads streamlines troubleshooting and fuse replacement. The right selection enhances voltage stability, reduces electromagnetic interference, and extends overall system longevity.
Technical Specifications and Safety Standards
In regulated industries, fuse holders must comply with UL, IEC, or SAE safety standards, ensuring consistent testing for dielectric strength, flammability, and current-carrying capacity. Reviewing datasheets for temperature ratings, maximum voltage, and contact resistance is vital. Certification labels facilitate regulatory acceptance, while traceability codes support quality audits. Verifying these specs prevents non-compliance issues and safeguards end-user reliability.
Related Inquiries
1、Which amp rating suits an automotive circuit?
Normal operating currents and expected surge levels guide ampacity choices. Select a holder rated slightly above the highest sustained load to avoid nuisance trips while ensuring fault protection.
2、How can I confirm holder size compatibility?
Compare the holder’s outer dimensions and panel cutout specifications against enclosure drawings. Check terminal types and wire gauge compatibility in the manufacturer’s datasheet.
3、What maintenance intervals are recommended?
Inspect fuse holders during routine service at least annually. Check for corrosion, secure connections, and housing integrity in demanding environments such as marine or industrial installations.

