Space-Saving Thermal Fuse Enhancing Protection In Confined Car Electrical Panels
News 2025-11-27
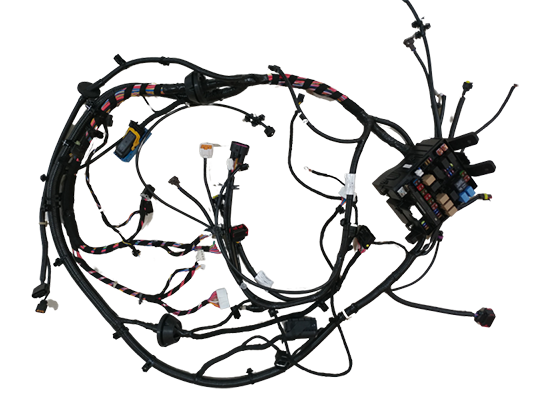
Compact thermal protection components play a decisive role in modern automotive electrical architectures, where wiring harness density and shrinking module sizes leave almost no room for bulky safety devices. A space-saving thermal fuse designed specifically for tight installations in car electrical panels addresses this challenge by combining fast response to overtemperature conditions and ease of integration. It improves protection of wiring, connectors, and semiconductor devices in areas where airflow is limited and heat buildup can quickly damage sensitive electronics.

Key Applications In Automotive Electrical Panels
Space-saving thermal fuses are widely used in body control modules, power distribution units, EV battery junction boxes, and infotainment control boards. These locations often host dozens of relays, MOSFETs, and DC‑DC converters packed into compact housings near high-current busbars. The miniature footprint of the fuse allows designers to position it close to the most heat-critical components, such as window-lift drivers, seat-heater circuits, fan motors, and LED lighting assemblies. In hybrid and electric vehicles, the fuse also helps safeguard auxiliary 12 V and 48 V rails where localized overheating may occur due to continuous high-load operation.
Performance Advantages And Design Characteristics
The compact thermal fuse combines a small package height with precise opening temperatures, often available across a range such as 72 °C to 240 °C to match different automotive derating strategies. Its low internal resistance minimizes power loss and self‑heating, supporting stable operation in densely populated PCBs. Fast thermal coupling between the fuse body and surrounding components ensures a quick response to abnormal temperature rise, preventing insulation damage or PCB delamination. Many versions meet automotive-grade requirements such as AEC‑Q200, exhibit robust vibration resistance, and feature flame-retardant encapsulation materials compatible with under‑dash and under‑hood environments.
Integration, Mounting Options, And Safety Compliance
To simplify engineering and manufacturing, space-saving thermal fuses are offered in radial leaded, axial leaded, or SMD configurations. Their compact geometry enables vertical or horizontal mounting in narrow gaps between harness connectors or adjacent modules in the fuse box. Designers can route the fuse in series with critical loads, use it as a backup layer to electronic overcurrent protection, or place multiple fuses in distributed locations to segment harness zones. Compliance with standards such as UL, VDE, and relevant automotive regulations supports certification of complete electrical panels, while clear marking of opening temperature and current rating reduces assembly errors during high-volume production.
Benefits For Vehicle OEMs, Tier Suppliers, And End Users
Automotive OEMs and module manufacturers benefit from higher packaging density without sacrificing safety margins. The compact fuse helps reduce module footprint, allowing more functionality in the same panel volume. It also contributes to longer service life of connectors, relays, and semiconductor switches by limiting thermal stress during abnormal operating conditions or partial failures. For end users, this translates into increased electrical system reliability, fewer nuisance failures in comfort features, and reduced risk of heat-related damage that could lead to costly repairs.
1. Typical trip temperature range
The space-saving thermal fuse can be selected across standardized opening temperatures, often between 72 °C and 240 °C, enabling precise matching to the thermal profile of each automotive circuit.
2. Difference between thermal fuse and resettable protector
A thermal fuse is a one-shot device that permanently opens when its rated temperature is exceeded, while resettable protectors such as PTCs return to normal after cooling but may not provide the same level of fail-safe isolation.
3. Placement recommendation in car panels
The fuse should be placed as close as possible to the most heat-sensitive components or potential hot spots on the PCB or harness branch, maximizing response accuracy and protecting both local circuitry and upstream wiring.