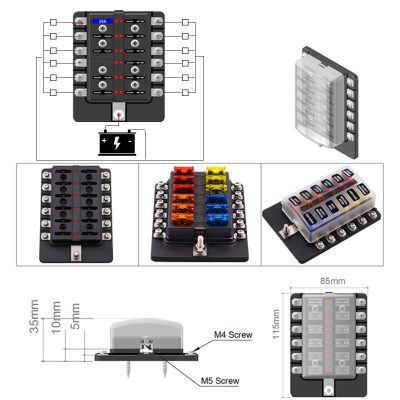
Warning Indicators In Fuse Box That Signal Impending Electrical System Breakdown
News 2025-12-25
Early warning signs inside a fuse box often decide whether an electrical system keeps running safely or suffers abrupt downtime. Identifying abnormal heat, discoloration, and erratic breaker behavior lets maintenance teams intervene before production halts, data centers go dark, or building safety systems lose power. In modern industrial and commercial environments, condition awareness in the distribution panel is now a performance topic, not just a safety requirement.
Thermal Clues And Visual Degradation
Hot spots on fuse holders, busbars, or terminal blocks are among the clearest indicators. Browned insulation, melted plastic near fuse clips, or a burnt odor point to sustained overload or poor contact resistance. In factories, elevated temperatures around motor feeders suggest undersized protection or loose terminations. Regular infrared thermography of fuse boxes in process plants, telecom shelters, and EV charging cabinets enables early detection, minimizing nuisance trips and unplanned shutdowns.
Irregular Operation And Nuisance Tripping
Frequent fuse blowing or repeated breaker operation under normal load conditions often signals deeper system stress. Causes include harmonic distortion from drives, unbalanced phases, and transient inrush currents from large compressors or UPS systems. When protective devices operate too often, contact surfaces erode and mechanical fatigue sets in, increasing the probability of total failure. Logging trip frequency and correlating it with load profiles helps engineers optimize coordination, select higher performance fuses, and stabilize mission‑critical applications.
Corrosion, Contamination And Mechanical Wear
Inside outdoor cabinets or high‑humidity sites, oxidation of terminals, greenish corrosion on copper, and dust accumulation across live parts degrade conductivity. Loose fuse clips, cracked insulation, and vibration‑induced wear in mobile equipment cabins change contact pressure and cause intermittent faults. For railway signaling, solar inverters, and marine electronics, using sealed fuse holders, corrosion‑resistant alloys, and vibration‑rated hardware extends system life and reduces unexpected outages, while keeping maintenance intervals predictable.
Monitoring Technologies And Performance Advantages
Modern fuse boxes can integrate temperature sensors, current transducers, and status LEDs to signal abnormal conditions long before a fault escalates. Remote monitoring over Ethernet or fieldbus lets facility managers track phase load, imbalance, and protection status in real time across industrial campuses. This approach enhances energy efficiency, avoids oversizing, and provides documented evidence for predictive maintenance. Upgraded protection architectures improve short‑circuit interrupt ratings, reduce arc‑flash risk, and increase uptime in data halls, automated warehouses, and medical imaging suites.
1. What causes fuse box components to overheat?
High contact resistance, sustained overload, and poor tightening torque generate localized heating at terminals and fuse clips, which accelerates insulation aging.
2. How often should fuse boxes be inspected in industrial plants?
Most facilities adopt at least annual inspections, while heavy‑duty or safety‑critical lines often use quarterly checks combined with periodic thermal imaging.
3. Are smart fuse boxes useful in small commercial buildings?
Yes, compact smart panels provide load visibility, early alarm functions, and reduced downtime, which benefits retail sites, offices, and small medical practices.