Accurate Temperature Response Thermal Fuse Ensures Precise Electronic Protection Performance
News 2025-11-27
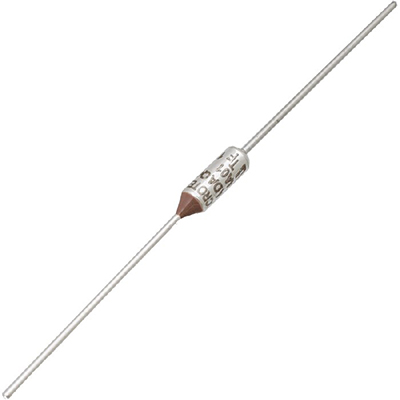
Accurate-temperature-response thermal fuses are engineered to disconnect a circuit exactly at the preset temperature, preventing damage caused by overheating and abnormal current conditions. Unlike generic thermal protectors that rely on wide tolerance bands, these fuses are designed for precise trip points that align closely with the thermal limits of semiconductors, batteries, and power conversion stages. Their fast and predictable operation makes them a core safety element in compact, high-density designs where even a few extra degrees can severely impact lifetime and reliability.
Construction, Working Principle, and Key Performance Metrics
Inside an accurate-temperature-response thermal fuse, a calibrated pellet or organic compound holds a spring-loaded contact in place. When the surrounding temperature reaches the specified threshold, the internal element melts or structurally changes, causing the contacts to open permanently and isolate the load. Critical performance parameters include opening temperature tolerance, holding temperature, rated current, and maximum interrupting capacity. Narrow temperature tolerance, often within ±3 °C, ensures that protection aligns tightly with component datasheet limits, while high interrupt ratings enable safe clearing of fault currents in power electronics and industrial systems.
Core Application Scenarios Across Modern Electronics
These fuses are widely deployed in AC adapters, LED drivers, telecom power supplies, EV onboard chargers, and energy storage systems where thermal stability directly impacts safety certification. In lithium-ion battery packs, accurate trip temperatures protect cells from runaway conditions triggered by overcurrent, blocked ventilation, or charging faults. In motor drives and HVAC controls, they safeguard coils, transformers, and control PCBs from insulation breakdown caused by hotspot development. Designers in household appliances, medical instruments, and smart meters integrate these devices close to heat sources on the PCB, ensuring a dependable last line of defense when active control loops or sensors fail.
Advantages Over Standard Thermal Protection Components
Compared with bimetal thermostats or resettable polymer devices, accurate-temperature-response thermal fuses provide a more sharply defined and reproducible opening temperature. Their one-time action adds a strong safety message: once a hazard occurs, the circuit remains disconnected until service personnel investigate the root cause. This reduces the risk of repetitive stress on power semiconductors, transformers, and wiring. The compact radial or axial packages support high power density layouts, while low internal resistance minimizes self-heating and power loss during normal operation. These attributes help design teams meet UL, IEC, and EN safety requirements without oversizing heat sinks or derating the entire system.
Design-In Considerations and Integration Best Practices
Selection of a thermal fuse starts by analyzing worst-case ambient conditions, component temperature ratings, and airflow within the enclosure. Engineers typically choose a fusing temperature slightly below the maximum permissible temperature of the most sensitive component, factoring in board-level thermal gradients. Correct mounting is critical: tight thermal coupling to the protected component or hotspot area ensures the fuse sees actual risk conditions in time. Coordination with upstream fuses or circuit breakers must be verified so that the thermal fuse clears safely under fault energy levels. Reliability testing, including temperature cycling and surge conditions, confirms long-term stability of the trip point and supports compliance documentation.
Application-Oriented Q&A
1How does a thermal fuse differ from a thermostat?
A thermal fuse provides irreversible protection at a defined temperature, while a thermostat cycles on and off to regulate temperature and can repeatedly reset.
2Where should a thermal fuse be placed on a PCB?
It should be mounted close to the primary heat source or the component with the strictest temperature limit, ensuring tight thermal coupling and fast response.
3Can accurate-temperature-response fuses be used in battery packs?
Yes, they are widely used in lithium-ion and NiMH battery packs to provide final overtemperature protection when charging circuits or BMS controls fail.


