Automotive Battery Box Solution for Compact Engine Bays and Constrained Spaces
News 2025-11-17
Modern vehicles with downsized engines and dense packaging demand energy storage hardware that occupies minimal space without sacrificing protection. An automotive battery box with a compact profile allows OEMs and system integrators to place high-capacity batteries in tight engine bays, under-seat locations, or trunk side pockets while maintaining compliance with thermal, electrical, and mechanical requirements. By optimizing enclosure geometry, cable routing, and mounting interfaces, these compact battery boxes help designers overcome space conflicts with cooling modules, ADAS sensors, and power electronics.
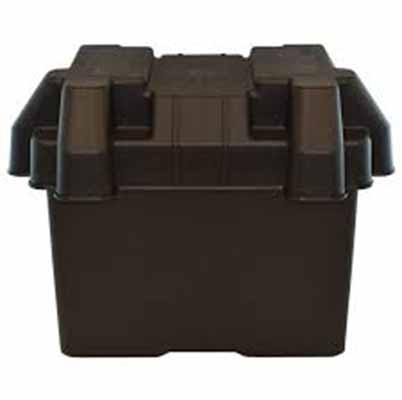

Compact Structure for Limited Engine Bay Space
A compact automotive battery box is engineered around strict envelope constraints commonly found in modern engine compartments. Low-height housings, contoured sidewalls, and corner radii are tailored to follow body sheet metal and surrounding components, maximizing usable volume for cells. High-strength lightweight materials, such as reinforced polymers or aluminum alloys, enable thinner walls while preserving impact resistance and structural rigidity. Integrated brackets and multi-point mounting reduce the need for bulky auxiliary hardware, freeing extra millimeters that are often decisive in crowded powertrain layouts.
Thermal Management and Electrical Performance
Even within a small footprint, the battery box must maintain stable operation over wide temperature and load ranges. Dedicated airflow channels, heat sinks, or liquid cooling interfaces can be incorporated without expanding the outer dimensions. This compact thermal architecture supports fast charging and high current discharge required by start-stop systems, mild hybrid architectures, and auxiliary power units. Optimized busbar design, short conductor paths, and low-resistance terminals minimize voltage drop and power loss, ensuring consistent cranking performance and efficient energy utilization across the vehicle’s electrical network.
Application Scenarios in Modern Vehicle Platforms
Space-saving battery boxes are suited for passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and specialty applications such as construction machinery or agricultural equipment where every centimeter under the hood is allocated. In EVs and hybrids, the compact profile enables secondary 12 V or 48 V batteries to coexist with traction battery packs and inverters in confined compartments. In retrofit and aftermarket projects, these enclosures simplify integration when original mounting points are unavailable, delivering an OEM-grade solution for fleets upgrading telematics, ADAS modules, or auxiliary lighting systems without redesigning the body structure.
Design Benefits for Durability, Safety, and Serviceability
A well-engineered compact battery box combines mechanical protection, environmental sealing, and ease of maintenance. Gasketed lids and precision-molded joints support IP-rated protection against water, dust, and road debris, even when the enclosure is mounted low in the engine bay. Reinforced corners and energy-absorbing zones shield the battery from vibration and shock loads encountered on rough roads. At the same time, quick-release latches, clearly marked polarity, and accessible service windows shorten replacement time in workshops, reducing vehicle downtime and total cost of ownership for fleet operators.
1. What vehicles benefit most from a compact battery box?
Passenger cars with small engine bays, hybrid and electric platforms, and commercial vehicles with dense under-hood packaging gain the most from compact battery box solutions.
2. Does the smaller profile affect battery safety?
No, when properly designed the compact box maintains impact resistance, ventilation, and insulation, meeting automotive safety and regulatory standards.
3. Can compact battery boxes support high-current applications?
Yes, optimized conductors, robust terminals, and efficient thermal paths allow compact enclosures to handle high cranking currents and frequent charge-discharge cycles.