Battery Box Solutions for 12V and 24V Automotive Power Storage and Protection
News 2025-11-17
Battery boxes compatible with 12 V and 24 V automotive battery systems play a key role in modern vehicles, off‑road platforms, and auxiliary power units. By combining mechanical protection, thermal management, and integrated connectivity, these enclosures help maintain stable performance for starting, lighting, ignition, infotainment, and aftermarket accessories. As vehicle electrical loads grow, choosing the right box for dual‑voltage or scalable configurations becomes a strategic decision for OEMs, fleet operators, and system integrators.

Key Design Features of Dual-Voltage Battery Boxes
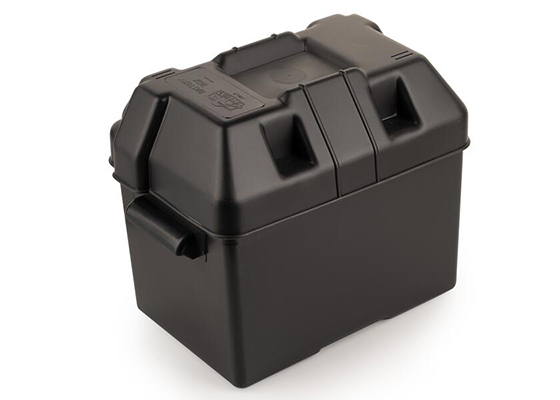
Battery boxes engineered for both 12 V and 24 V configurations must support a wide range of form factors, including DIN, JIS, and deep‑cycle batteries. Robust housings use impact‑resistant plastics or coated steel, with reinforced lids and secure latching to handle vibrations from commercial vehicles, RVs, and utility trucks. Integrated knockout ports and cable glands simplify routing for series or parallel connections, enabling straightforward upgrades from 12 V to 24 V systems. Venting channels or hose connectors help disperse gases from flooded lead‑acid batteries, while sealed designs support AGM, EFB, and lithium chemistries. Corrosion‑resistant hardware and UV‑stable materials extend service life in engine compartments, chassis rails, and exterior mounting points.
Performance Benefits in Automotive and Off-Highway Applications
Well‑designed battery boxes directly enhance system performance by stabilizing electrical output in harsh environments. Secure mounting reduces micro‑vibration that can damage internal battery plates, improving cycle life and cold‑cranking capability in 12 V starter batteries. For 24 V applications such as heavy trucks, construction equipment, and agricultural machinery, optimized cable routing and terminal access minimize voltage drop and heat buildup under high current loads. Thermal management features, including ventilation slots and optional insulation, help maintain optimal battery temperatures during high load operation or rapid charging from alternators and DC‑DC converters. These characteristics translate into fewer unexpected failures, longer replacement intervals, and more consistent energy delivery to ECUs, sensors, and auxiliary power systems.
Typical Use Cases and Integration Scenarios
Dual‑compatible battery boxes are widely used in passenger cars with upgraded audio systems, camper vans with 12 V house batteries, and commercial fleets requiring 24 V starting and 12 V cabin power through DC‑DC conversion. They are also common in emergency vehicles, telematics gateways, mobile surveillance systems, and power backup units for tolling or ITS infrastructure. Modular box designs allow installers to combine two 12 V batteries in series for 24 V applications, or maintain separate banks for starter and auxiliary loads. Pre‑molded mounting points, fuse holders, and busbar options accelerate integration with smart battery sensors, battery management systems, and solid‑state relays. This flexibility supports both OEM manufacturing lines and aftermarket retrofits where installation time and serviceability are critical.
Selection Criteria, Safety, and Maintenance Considerations
When selecting a battery box for 12 V and 24 V systems, engineers should verify compliance with automotive vibration and flammability standards, ingress protection ratings, and compatibility with planned cable sizes and connector types. Adequate clearance around terminals is important for safe torqueing and insulation, reducing the risk of short circuits during installation or maintenance. Boxes with clear labeling areas and color‑coded grommets simplify identification of positive and negative rails in multi‑battery systems. For vehicles exposed to road spray, salt, and mud, sealed lids and drain features help protect against moisture intrusion and conductive contamination. Regular inspection of mounting bolts, vent paths, and cable strain reliefs ensures that the protective function of the battery box is maintained over the entire service life of the vehicle.
1. What vehicles typically use 24 V battery box configurations?
24 V battery box setups are common in heavy‑duty trucks, buses, military vehicles, construction machinery, and large agricultural equipment that require high starting current and stable power for multiple electronic control units.
2. Can one battery box support both 12 V and 24 V systems?
Yes, many boxes are designed to house one or two 12 V batteries, allowing installers to configure them in series for 24 V or use a single unit for 12 V, provided that dimensions, cable routing, and venting meet the application requirements.
3. Are these battery boxes suitable for lithium batteries?
Most modern automotive battery boxes support AGM and lithium batteries as long as they meet size and terminal standards; for lithium packs, users should confirm BMS integration, ventilation needs, and mechanical mounting compatibility with the chosen enclosure.