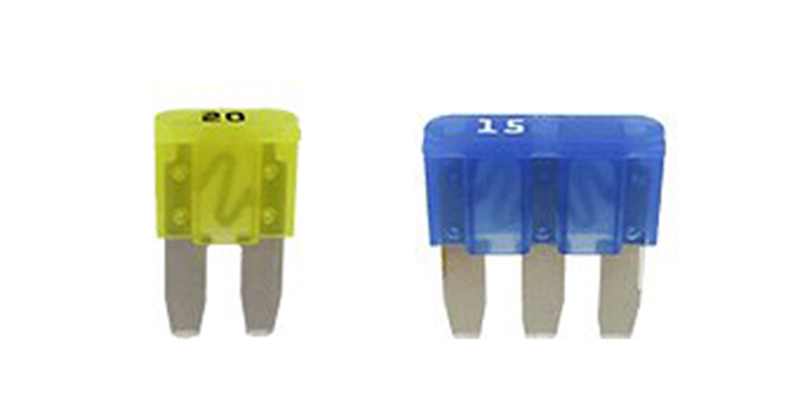
Climate Control Fuse Enhances Protection Of Automotive AC And Heating Circuits
News 2025-11-17
An automotive climate control system depends on stable electrical power to drive blowers, compressor clutches, actuators, sensors, and the electronic control unit. Within this network, the climate control fuse acts as a deliberate weak link that disconnects power when current exceeds a safe threshold. By interrupting fault currents caused by short circuits, insulation failure, or component aging, the fuse protects wiring looms, control modules, and cabin comfort devices from overheating damage, smoke, or fire. This small component is therefore a fundamental safety and reliability element in both passenger and commercial vehicles.
Key Function And Operating Principle
A climate control fuse is calibrated to open the circuit at a specific current level and time profile. Under normal operation, the fuse element carries the rated current to the AC compressor clutch, blower motor, HVAC control panel, and auxiliary fans without excessive temperature rise. When a fault occurs, the resulting surge in current rapidly heats the fusible link until it melts, creating a non-conductive gap and isolating the faulted section. Modern blade, mini-blade, and low-profile fuse formats are designed for tight automotive fuse boxes, providing clearly marked ratings that simplify service and diagnostics. Correct selection of current rating and interrupting capacity prevents nuisance blowing while still ensuring robust circuit protection.
Application Scenarios In AC And Heating Systems
In everyday driving, the climate control fuse protects several high-demand loads. The blower motor circuit draws substantial current at high fan speeds; a seized motor bearing or obstructed fan wheel can cause a sharp current increase that immediately challenges the fuse. The compressor clutch circuit experiences frequent cycling, especially in hot climates, and a damaged harness or clutch coil can result in a direct short to ground. Electronic HVAC control modules, temperature sensors, and damper actuators depend on low-current fused feeds that shield sensitive semiconductors from overcurrent conditions originating in shared supply lines. In electric and hybrid vehicles, separate fuses may safeguard high-voltage electric compressors and PTC heaters, integrating into sophisticated thermal management architectures.
Performance Advantages And Design Considerations
High-quality climate control fuses deliver tight tolerance on current rating, stable performance over a wide temperature range, and proven vibration resistance suitable for engine compartment and dashboard locations. Low internal resistance reduces I²R losses, supporting energy efficiency and minimizing heat buildup inside compact fuse blocks. Engineers typically choose automotive-grade fuses that comply with ISO and SAE standards, ensuring consistent behavior under repeated thermal cycling and harsh environmental exposure. Proper coordination between climate control fuses and upstream protection devices prevents cascading failures while allowing straightforward fault isolation, which shortens diagnostic time in service centers and supports higher vehicle uptime.
Maintenance, Troubleshooting, And Replacement Practices
From a maintenance perspective, a blown climate control fuse is both a symptom and a protective action. Technicians should investigate root causes such as damaged wiring harnesses behind the dashboard, corrosion in connectors leading to the blower or compressor clutch, or internal short circuits in the HVAC control head. Using the correct fuse type and rating specified by the vehicle manufacturer is vital; oversizing a fuse may temporarily stop nuisance failures but exposes the climate control circuit to serious overheating risk. High-visibility fuse bodies and clear ampere markings help workshops and fleet operators manage replacements quickly while reducing errors. As vehicles integrate more electronic climate functions, demand grows for fuses that combine high interrupting ratings, compact footprints, and long-term stability.
1. Why does my AC stop working when the climate control fuse blows?
The blown fuse cuts power to the AC compressor, blower, or control unit, preventing current from flowing in a faulted circuit. This protects wiring and components, but it also disables cooling until the underlying problem is repaired and the correct fuse is replaced.
2. Can I use a higher-rated fuse in the climate control circuit?
Using a higher-rated fuse than specified is unsafe. It allows excessive current to flow without interruption, which can overheat cables, damage the HVAC module, and increase fire risk. Always match the rating in the service manual or on the fuse box label.
3. What symptoms indicate a failing climate control fuse or circuit?
Common symptoms include an inoperative blower fan, AC compressor that never engages, intermittent operation of the HVAC panel, or repeated fuse blowing shortly after replacement. These signs usually indicate an underlying wiring fault, shorted motor, or defective control module.