Connection Loosening Effects On Fuse Box Integrity And Vehicle Electrical Function
News 2025-12-23
Modern vehicles depend on stable electrical distribution to support safety, comfort, and control systems. The fuse box acts as the central hub that routes power from the battery to lighting, engine management, infotainment, and driver‑assistance modules. When connections inside this hub begin to loosen, performance issues appear gradually, then escalate into intermittent faults, component damage, or unexpected shutdown of critical loads.
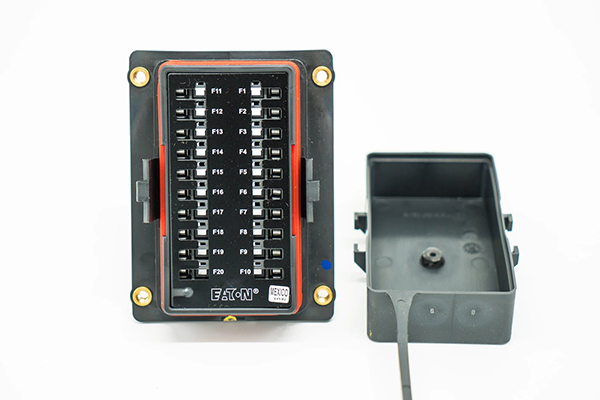

Typical Causes Of Loose Fuse Box Connections
Vehicle fuse boxes operate in harsh environments: constant vibration, thermal cycling, moisture, and dust. Loose connections often arise from insufficient terminal crimp force, aging and oxidation of contact surfaces, plastic housing deformation, or improper fuse insertion during service. High under‑hood temperatures accelerate creep of plastics and soften spring contacts, reducing clamping force on blade fuses. In high‑mileage vehicles or commercial fleets, repeated load peaks and current surges can also cause micro‑arcing that erodes contact plating, further weakening the mechanical fit and electrical continuity.
Impact On Electrical Performance And Safety
A slightly loose connection raises contact resistance, which leads to localized heating under load. Over time, the hot spot darkens the fuse cavity, warps the terminal, and may cause nuisance fuse blowing. Drivers notice symptoms such as flickering headlamps, unstable instrument clusters, random reset of infotainment systems, malfunctioning wipers, or disabled auxiliary heaters. In severe cases, power supply to the engine control unit becomes unstable, triggering fault codes, limp‑home mode, or engine stall. The combination of heat, arcing, and plastic deformation may even bypass proper fuse operation, undermining circuit protection and safety compliance.
Application Scenarios And Performance Benefits Of Robust Designs
Passenger cars, heavy trucks, construction machinery, and agricultural vehicles all place different demands on fuse box assemblies. Off‑highway equipment encounters extreme vibration and dirt, making high‑retention terminals and sealed fuse boxes a key design priority. In urban electric vehicles, compact packaging and high current traction circuits require low‑resistance contacts and optimized thermal paths. Using high‑spring‑force terminals, tin or silver plating, and glass‑fiber‑reinforced housings helps maintain contact pressure over the entire vehicle lifetime. The performance benefits include stable voltage at sensitive control units, reduced warranty claims, fewer unexplained warning lights, and improved uptime for fleet operators.
Design, Testing, And Maintenance Recommendations
Engineers should validate fuse box designs through vibration, thermal shock, and current cycling tests that simulate real driving profiles. Monitoring contact resistance and temperature rise under maximum load helps identify weak links before series production. During service, technicians should inspect for discoloration, melted plastic, and fuses that are easy to wiggle, then restore integrity by replacing damaged terminals or the entire board. Using torque‑controlled fasteners on main power feeds, applying contact‑safe protective sprays, and keeping moisture away from the housing further limit loosening over time.
1. How can drivers detect early signs of loose fuse box connections?
Intermittent operation of lights or accessories, occasional warning messages that clear after restart, and localized burning smell near the dashboard or engine bay are typical early indicators that warrant inspection.
2. Which vehicle applications face the highest risk of connection loosening?
Vehicles exposed to strong vibration or frequent load peaks, such as delivery vans, heavy trucks, mining equipment, and agricultural machinery, face higher risk and benefit most from reinforced fuse box designs.
3. What maintenance action offers the greatest performance improvement?
Systematic inspection during scheduled service, cleaning of oxidation, replacing heat‑damaged fuses and terminals, and ensuring correct seating of every fuse provide the largest improvement in electrical stability and long‑term vehicle reliability.