Consistent-Performance Thermal Fuse Enables Stable Protection In Diverse Electronic Systems
News 2025-11-27
Consistent-Performance Thermal Fuse Delivers Reliable Protection Across Use Cases
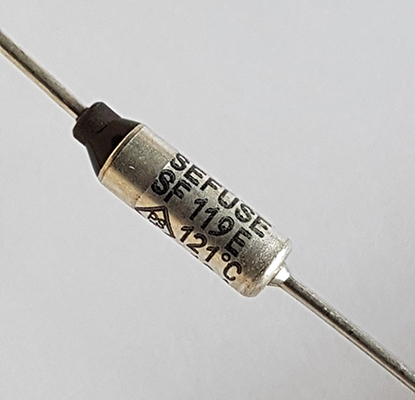

Stable Protection In Demanding Applications
Thermal fuses designed for consistent performance have become a key safeguard in compact, high-density electronic assemblies. Unlike resettable devices, they provide a one-time, precisely defined cutoff when abnormal temperature rise threatens system integrity. In switch-mode power supplies, LED drivers, and battery chargers, a narrow tolerance on opening temperature is crucial to prevent damage to semiconductors and surrounding materials. The fuse must respond quickly enough to interrupt fault energy, yet remain stable during normal load and moderate ambient fluctuations. This balance enables designers to meet safety standards such as UL, IEC, and EN while keeping layouts simple and cost effective.
Key Performance Characteristics That Matter
The core value of a consistent-performance thermal fuse lies in predictable opening temperature, rated holding current, and low resistance. By maintaining tight temperature calibration across production lots, the device activates at nearly the same point in every unit, which simplifies derating calculations and worst-case analysis. Low internal resistance supports energy efficiency and reduces self-heating in high-current lines feeding motor drives, inverter boards, and heater controls. Long-term stability under thermal cycling and surge loading ensures that the fuse does not drift or fatigue during years of operation. These attributes help maintain uptime, extend product life, and protect expensive components from irreversible thermal runaway events.
Application Scenarios Across Multiple Sectors
Consistent-performance thermal fuses are widely deployed in home appliances, HVAC controllers, industrial power modules, and consumer electronics. In coffee machines, hair dryers, and electric heaters, they sit close to heating elements to cut power if temperature rises beyond design limits. In lithium-ion battery packs and energy storage systems, they serve as a final thermal barrier that complements electronic battery management circuitry. Telecommunications equipment and 5G infrastructure integrate them on power distribution boards to prevent localized overheating that could interrupt network availability. Automotive electronics, such as on-board chargers and DC-DC converters in electric vehicles, also benefit from their stable response under vibration, wide ambient ranges, and frequent load transients.
Design Integration And Compliance Benefits
Engineering teams value thermal fuses that simplify layout and certification. Compact radial or axial packages allow easy placement close to heat sources, while standardized lead forms support automated assembly and wave soldering. Using components tested against major global safety standards streamlines system-level approvals and reduces time to market. Clear datasheet parameters such as opening temperature range, current rating, interrupting capability, and thermal profile help designers perform accurate derating and fault tree analysis. When consistent performance is validated through statistical process control and 100% testing, OEMs gain greater confidence during warranty planning, field reliability projections, and long-term service commitments.
Selection Tips And Future Trends
Choosing an appropriate thermal fuse requires aligning opening temperature with the maximum allowable component and board temperature, while accounting for ambient variation and airflow. Engineers should confirm that the holding current exceeds normal operating current under worst-case conditions, yet remains compatible with the chosen setpoint. Mounting position, insulation, and proximity to heat sources directly affect response time, so thermal modeling and targeted lab testing remain advisable. As power densities continue to rise in GaN- and SiC-based systems, demand grows for fuses that combine narrow tolerance, higher operating temperature capability, and enhanced mechanical robustness. Devices delivering consistent performance across these evolving conditions will continue to play a central role in electronic protection strategies.
1What role does a thermal fuse play in a power supply?
It disconnects the circuit permanently if internal temperature exceeds a defined threshold, preventing damage to magnetic components, semiconductors, and insulation.
2How is a thermal fuse different from a thermostat?
A thermal fuse opens once and must be replaced, while a thermostat or thermal switch resets automatically and can cycle on and off many times.
3Where should a thermal fuse be placed on a PCB?
It should be located close to the most critical heat source or hot spot, with minimal thermal barriers, so that it senses abnormal temperature rise quickly and accurately.