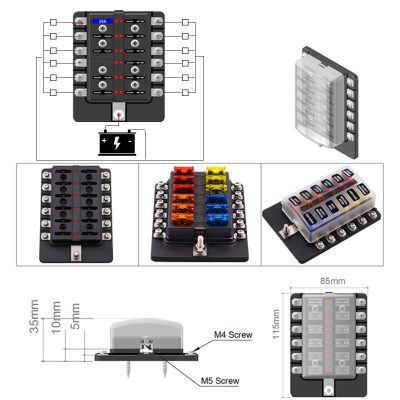
Corrosion-Proof Fuse Coating Enhances Safety in Harsh Humid Environments
News 2025-11-17
Corrosion-proof coatings tailored for fuses have become a key enabler in modern electrical systems operating in harsh humidity. Moist air, condensation, and airborne salts rapidly attack unprotected metal contacts, leading to increased resistance, overheating, and eventually nuisance or dangerous fuse failures. By forming a stable, moisture-resistant barrier over conductive elements and terminations, the special coating described here significantly extends fuse service life while maintaining consistent electrical performance in demanding applications.
Core Material Science Behind the Anti-Rust Coating
This corrosion-proof fuse coating uses a hybrid inorganic–organic matrix engineered to block oxygen, water molecules, and aggressive ions. Nano-scale fillers tighten the barrier structure, reducing permeability without adding excessive thickness. The formulation maintains low surface energy, preventing moisture film formation that would otherwise trigger galvanic corrosion on fuse end caps, blades, and clips. The coating is optimized to withstand thermal cycling typical of fuse operation, preserving adhesion and preventing micro-cracks that could expose bare metal. Careful selection of resins and additives keeps leakage current extremely low, protecting insulation resistance even after long exposure to 95% relative humidity or salt-mist environments.
Key Performance Benefits Under Humid and Condensing Conditions
In accelerated humidity tests, coated fuses maintain stable contact resistance and demonstrate minimized oxidation on critical surfaces. This stability reduces localized heating at contact points, improving current-carrying capacity and limiting derating in dense power distribution panels. The fuse coating resists blistering, peeling, and discoloration, allowing predictable time–current characteristics over the product lifetime. Maintenance intervals can be extended because users experience fewer corrosion-induced open circuits or intermittent connections. Compared with uncoated devices, field data typically shows lower failure rates in coastal areas, tropical climates, wastewater facilities, and greenhouses where condensation and chemical vapors are prevalent.
Application Scenarios in Industrial, Automotive, and Energy Systems
This special anti-rust coating is particularly valuable in outdoor switchgear, photovoltaic combiner boxes, wind turbine nacelles, and telecom base stations exposed to year-round humidity and temperature swings. In transportation, it protects fuses in engine compartments, underbody junction boxes, and marine control panels where salt spray and road chemicals accelerate corrosion. Building automation, HVAC units, and smart metering cabinets also benefit, as the coating helps maintain stable protection levels in basements, rooftops, and unconditioned spaces. Designers focused on high uptime and low service costs can specify coated fuses to improve system resilience, especially when equipment must comply with stringent safety and reliability standards in corrosive atmospheres.
Integration, Standards Compliance, and Design Considerations
The corrosion-proof coating is engineered to be fully compatible with common fuse body materials, including ceramic, glass, and high-temperature polymers, as well as tin-, silver-, or nickel-plated terminations. It is applied in tightly controlled layers to avoid altering fuse dimensions, ensuring seamless fit into existing clips, holders, and modular carriers. The coating process is validated so that fuses continue to meet IEC and UL interruption ratings, dielectric strength, and temperature-rise limits. Electrical designers should consider environmental severity, enclosure IP rating, and expected maintenance access when choosing coated versions. In high-humidity markets, specifying these coated fuses enhances product value and strengthens compliance arguments regarding long-term safety under real operating conditions.
FAQs on Corrosion-Proof Fuse Coating
1. How does the coating impact electrical performance?
The coating is formulated to keep contact resistance low and stable, while maintaining insulation resistance and dielectric strength. Proper application ensures that time–current characteristics and breaking capacity remain within standard specification limits.
2. Where is this coating most beneficial?
It delivers the greatest benefit in coastal regions, tropical climates, agricultural facilities, marine systems, and outdoor power or communication cabinets where high humidity, salt, or chemical vapors commonly attack metallic fuse parts.
3. Does the coating change installation or maintenance procedures?
Installation remains the same as for standard fuses, as dimensions and terminal geometry are preserved. Maintenance intervals can often be extended because corrosion-related failures and contact cleaning requirements are significantly reduced.