High-Precision-Tripping Thermal Fuse Meets Exacting Vehicle Safety Requirements in Harsh Environments
News 2025-11-27
High-Precision-Tripping Thermal Fuse Meets Exacting Vehicle Safety Requirements in Harsh Environments

Meeting Stringent Automotive Safety and Compliance Demands
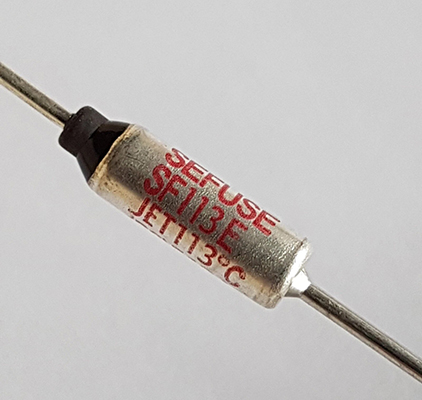
The high-precision-tripping thermal fuse is engineered to satisfy demanding vehicle safety standards in combustion engine, hybrid, and battery-electric platforms. It is designed as a single-use, temperature-sensitive cutoff that interrupts current once a predefined trip point is reached, preventing overheating, thermal runaway, and secondary damage. By combining a tightly controlled melting alloy and low-resistance terminals, the device maintains normal operation during everyday temperature fluctuations, then disconnects sharply when abnormal heat appears. This behavior aligns closely with the qualification needs of ISO 26262 functional safety concepts and common OEM design rules for onboard protection.
Application Scenarios in Modern Vehicle Architectures
The fuse plays a key protection role in power battery packs, on-board chargers, DC-DC converters, e-compressors, PTC heaters, and seat or steering wheel heating modules. In high-voltage battery systems, it acts as a last line of defense near cell groups or sensing modules where localized hotspots may occur. In 12 V and 48 V systems, it protects motor windings, relay coils, and MOSFET-based control boards from sustained overtemperature conditions that conventional circuit breakers may not detect. Mechanical compactness allows direct integration into wiring harnesses, sensor modules, and control units, enabling focused thermal monitoring close to critical components without sacrificing space in crowded automotive assemblies.
Performance Advantages and Precision Tripping Characteristics
The main strength of this thermal fuse lies in its narrow trip-temperature tolerance and repeatable fusing characteristics. Typical rated responses fall within a few degrees Celsius, permitting engineers to align cutoff thresholds precisely below the maximum safe temperature of insulation materials, electrolyte chemistries, or semiconductor junctions. Low contact resistance minimizes power loss and self-heating, maintaining accuracy even under high continuous current. Robust mechanical crimping and encapsulation processes deliver high vibration endurance and moisture resistance. These properties help preserve calibration over vehicle lifetime, which is vital in engine compartment and underfloor battery environments where heat cycles and road shocks are constant.
Design Integration, Assembly, and Quality Assurance Considerations
From an assembly standpoint, the fuse supports automated soldering or crimping processes, simplifying integration into existing harness and PCB production lines. Clear marking of rated temperature and current enables traceability in global supply chains and supports detailed DFMEA documentation. Device selection should consider ambient temperature range, mounting position, and thermal coupling to the target component to ensure correct correlation between hotspot temperature and fuse body temperature. Suppliers typically offer PPAP documentation, AEC-Q compliant testing, and 100% electrical inspection to match OEM quality requirements. Early involvement in system design allows optimization of both thermal path and electrical rating, reducing the risk of nuisance trips while still providing reliable cutoff under fault conditions.
FAQ: High-Precision-Tripping Thermal Fuse in Vehicle Safety
1. Where is this thermal fuse most commonly used in vehicles?
It is widely used in battery modules, on-board chargers, HVAC blowers, seat heaters, and power electronics to prevent overheating and component damage.
2. How does the precise trip temperature help designers?
Tight temperature tolerance lets engineers set the fuse just below the maximum safe operating limit, improving protection without causing premature interruption.
3. Can the fuse be reset after activation?
No. It is a non-resettable device that must be replaced once it has opened, ensuring that any severe overtemperature event is treated as a serviceable fault.