High-Temperature-Rated Thermal Fuse Handles Demanding Vehicle Electrical Loads In Modern E-Mobility Systems
News 2025-11-27
High-temperature-rated thermal fuses are becoming a key protection component in modern automotive electrical architectures, where dense packaging, powerful loads, and elevated under-hood temperatures converge. From electric power steering and battery management units to on-board chargers and heated seats, these one-shot safety devices interrupt current once a defined temperature threshold is reached, preventing wiring damage, connector deformation, and potential fire hazards. Their compact footprint and precise fusing characteristics enable designers to safeguard individual subcircuits without sacrificing valuable PCB or harness space.
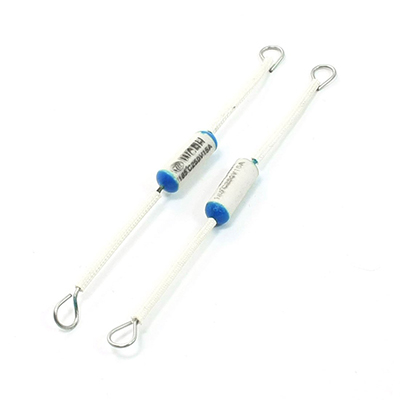

Key Performance Characteristics in Harsh Environments
High-temperature-rated thermal fuses are engineered to operate in ambient conditions that often exceed 150°C near engine compartments or traction inverters. Typical models specify holding temperatures well above standard consumer-grade parts, while offering accurate opening temperatures in a narrow tolerance band. Low contact resistance helps minimize power loss and heat generation during normal operation, which is crucial in high-current automotive lines. Automotive-grade versions are qualified to AEC-Q200 or equivalent standards and support robust surge capability, vibration resistance, and long-term thermal stability, ensuring predictable behavior over the vehicle lifetime.
Automotive Application Scenarios and Integration
In passenger vehicles and commercial EVs, thermal fuses protect AC and DC subsystems such as PTC heaters, blower motors, seat and steering-wheel heaters, auxiliary pumps, as well as USB fast-charging hubs. They are often placed in series with the load or upstream of DC/DC converters to act as the last line of protection when electronic control fails or software-based limits are bypassed. Designers can integrate high-temperature fuses into junction boxes, smart power distribution modules, or directly within wiring harness splices. Their predictable trip temperature simplifies coordination with NTC sensors, MOSFET switches, and resettable overcurrent devices, creating layered protection schemes that balance safety and serviceability.
Design Considerations and Selection Criteria
Selecting a suitable high-temperature thermal fuse requires careful evaluation of continuous load current, inrush profiles, ambient thermal conditions, and surrounding materials. Engineers must verify that the rated opening temperature sits above normal operating peaks yet stays below the maximum allowable temperature for insulation, connectors, and nearby components. Thermal modeling and placement studies help ensure the fuse senses actual hotspot conditions rather than artificially cooled or heated regions. Key datasheet parameters include rated current, maximum interrupting current, cold resistance, and time-to-open curves measured under specified test currents. Compliance with ISO 26262 functional safety concepts can be supported by derating the fuse, applying redundancy in safety-critical nodes, and documenting failure mode behavior.
Benefits for Safety, Compliance, and Efficiency
Compared to solely relying on electronic overcurrent protection, high-temperature thermal fuses provide an independent, non-resettable safeguard that is immune to firmware bugs and diagnostic failures. Their fast thermal response helps limit damage during prolonged overloads, locked-rotor motor conditions, or connector failures that create local hotspots. The compact, cost-effective nature of these components supports scalable platform designs spanning 12 V, 24 V, and high-voltage EV architectures. By enhancing protection against thermal runaway events and enabling compliance with OEM and regulatory safety requirements, they contribute directly to vehicle reliability metrics, warranty cost reduction, and customer confidence in electrified powertrains.
1、What differentiates a high-temperature-rated thermal fuse in automotive use?
High-temperature-rated thermal fuses are designed to maintain stable performance in elevated ambient conditions while delivering precise opening temperatures and high interrupt ratings suitable for demanding vehicle loads.
2、Where are these thermal fuses typically installed in vehicles?
They are commonly installed in heater circuits, motor drives, battery-related subsystems, and power distribution modules, usually in series with the protected load or upstream of conversion stages.
3、How should engineers approach selecting the correct fuse rating?
Engineers should analyze worst-case current, ambient temperature, thermal rise, and insulation limits, then choose a fuse that opens below critical component temperature ratings yet above normal operating peaks, applying appropriate safety margins and derating.