Lightweight Sturdy Battery Box Solutions for Electric Vehicle Auxiliary Power Systems
News 2025-11-17
Lightweight sturdy battery box electric vehicle auxiliary batteries are becoming a key design focus as EV platforms add more electronic subsystems. Navigation units, telematics gateways, ADAS controllers, pumps, actuators, and smart lighting all depend on stable low-voltage power that cannot always be guaranteed by the traction battery alone. A dedicated auxiliary battery module housed in a mechanically robust yet lightweight enclosure helps separate safety‑critical loads, improve power quality, and simplify wiring architecture across the vehicle.

Mechanical Design and Structural Integrity
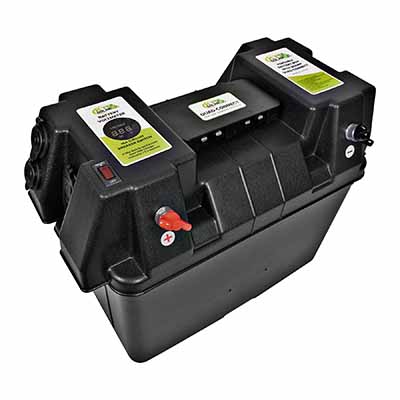
A modern auxiliary battery box for electric vehicles must withstand vibration, impact, road salt, and thermal cycling over many years. Engineers increasingly use high-strength aluminum alloys or glass‑fiber reinforced polymers to achieve a low mass-to-strength ratio. Ribbed geometries, finite element optimization, and well‑placed mounting bosses ensure that the box resists deformation under crash loads and complies with automotive standards such as ISO 16750. Precision sealing surfaces and stainless fixings maintain enclosure rigidity while allowing repeated service access without compromising structural stability.
Thermal Management and Electrical Safety
Auxiliary batteries powering ECUs and actuators generate heat during charge and discharge, especially in compact EV platforms with limited airflow. Battery boxes integrate ventilation channels, flame‑retardant internal spacers, and optional heat spreaders or phase‑change pads to keep cell temperature in the optimal band. The enclosure also supports fuse holders, current sensors, and insulation barriers to manage short‑circuit risks. High dielectric‑strength materials, creepage‑and‑clearance control, and clearly marked service points help technicians work safely while maintaining compliance with ISO 26262 functional safety requirements.
Application Scenarios in Modern Electric Vehicles
Lightweight, sturdy auxiliary battery boxes appear in multiple EV domains, from passenger cars to last‑mile delivery vans and off‑highway equipment. Typical applications include supplying stable 12 V or 24 V power to brake control units, steering systems, e‑call modules, keyless entry, and parking assistance sensors. In fleets, rugged enclosures enable external mounting under the chassis or on roof racks for telematics and video recording units. For construction and mining vehicles, dust‑tight and water‑resistant housings allow auxiliary packs to support hydraulic pumps and lighting towers in harsh outdoor environments without compromising uptime.
Performance Benefits and Integration with Vehicle Architecture
Using a lightweight yet robust battery box reduces overall vehicle mass, supporting longer driving range while maintaining structural safety margins. Optimized packaging shortens cable runs, cutting resistive losses and simplifying wiring harness design. Modular enclosure footprints let OEMs scale capacity from small auxiliary packs for city cars to higher‑energy modules for commercial EVs with heavy accessory loads. Mounting interfaces aligned with common EV platforms speed up production and enable flexible placement near high‑priority loads, improving voltage stability during dynamic operating conditions.
1What materials are commonly used for EV auxiliary battery boxes?
High-strength aluminum, stainless steel hardware, and glass‑fiber or carbon‑fiber reinforced polymers are widely used to balance low weight with durability, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability.
2Where are auxiliary battery boxes typically installed in an electric vehicle?
They are often mounted in the front compartment, under seats, beneath the floor, or on protected underbody rails, depending on crash requirements, cooling strategy, and cable routing.
3How does a rugged battery box improve system reliability?
It protects cells and electronics from vibration, moisture, dust, and impact, maintains stable temperatures, and integrates fusing and isolation features that reduce failure rates across the auxiliary power network.