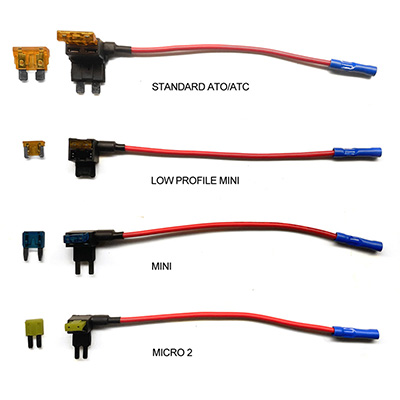
Power window fuse safeguards window motor and switch connections in modern vehicles
News 2025-11-17
Power window fuse safeguards window motor and switch connections
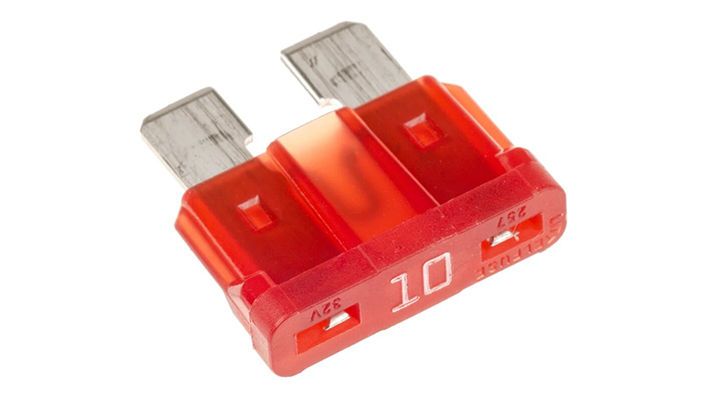

Role of the power window fuse in automotive systems
The power window fuse acts as a dedicated safety barrier between the vehicle’s electrical supply, the window motor, and the control switches. It is engineered to open the circuit rapidly when abnormal current levels appear, typically caused by short circuits, jammed glass mechanisms, or damaged wiring in the door harness. By interrupting current before wiring overheats, the fuse protects the motor windings, connector terminals, and nearby plastic parts from thermal damage and potential fire risk. In modern vehicles that integrate body control modules, correct fuse coordination also avoids costly failures of driver-side master switch assemblies and electronic control units.
Application scenarios across passenger, commercial, and specialty vehicles
Power window fuses are widely deployed in passenger cars, SUVs, light trucks, and premium commercial vehicles where comfort and safety features are integrated into every door. They safeguard circuits in single-touch auto up/down systems, child safety lock configurations, and smart key remote window closing functions. In fleet and utility vehicles, robust fuse ratings protect heavily used door windows exposed to dust, moisture, and frequent operation cycles. Specialty applications, such as armored vehicles, limousines, and off-road models, often specify higher-capacity motors and heavier glass, making precise fuse selection vital to avoid nuisance trips while still preventing thermal overload in extreme environments.
Performance advantages, ratings, and selection considerations
A well-matched power window fuse improves system stability by balancing protection speed and operational continuity. Typical blade or mini-blade fuses used in window circuits are rated between 20 A and 40 A, chosen based on motor inrush current, continuous load, wire gauge, and ambient temperature inside the door cavity. High-quality fuses feature low internal resistance, consistent time-current characteristics, and strong vibration tolerance, which supports long-term reliability under road shock. Engineers evaluate stall current of the lift motor, friction of the regulator, and expected duty cycle to define an appropriate fuse margin. Accurate matching reduces unexpected fuse blows in winter icing conditions while still protecting wiring looms during severe faults.
Integration in wiring harness, diagnostics, and maintenance
In practical applications, the power window fuse is usually located in a centralized fuse box or body control fuse panel, enabling quick access for diagnostics and service. Clear labeling on the panel and on service documentation helps technicians identify the correct fuse when troubleshooting inoperative windows. During diagnosis of a non-moving window, technicians verify fuse continuity first, then inspect the motor, switches, and door harness for shorts, corrosion, or water ingress. High-visibility fuse designs assist visual inspection, and standardized footprints streamline replacement using automotive-grade components that meet ISO and OEM specifications, sustaining consistent protection performance throughout vehicle life.
Three short Q&A on power window fuses
1. Why does the power window fuse blow repeatedly?
Frequent fuse failure usually indicates a shorted motor, pinched door harness, or excessive mechanical resistance in the regulator that drives current above the fuse rating.
2. Can a higher-amp fuse be installed to stop nuisance blowing?
Using a higher-amp fuse than specified is not recommended, as it can allow dangerous overheating of wires and connectors before the fuse responds.
3. How often should the power window fuse be replaced?
The fuse does not require periodic replacement; it should only be replaced after a fault is corrected and the cause of the overcurrent has been verified and removed.