Thermal Fuse: Reliable Overheat Protection for Diverse Applications
Introduction
A thermal fuse is a critical overheat protection component designed to interrupt electrical circuits when temperatures exceed a predefined threshold, preventing equipment damage and fire hazards. Widely used in electronics, automotive, household appliances, and industrial machinery, thermal fuses offer reliable safety solutions with different temperature ratings, current capacities, and package types to meet diverse application needs. Whether for consumer devices like microwaves and hair dryers or industrial equipment such as motors and transformers, choosing the right thermal fuse ensures operational safety and compliance with industry standards.

What is a Thermal Fuse and How Does It Work?
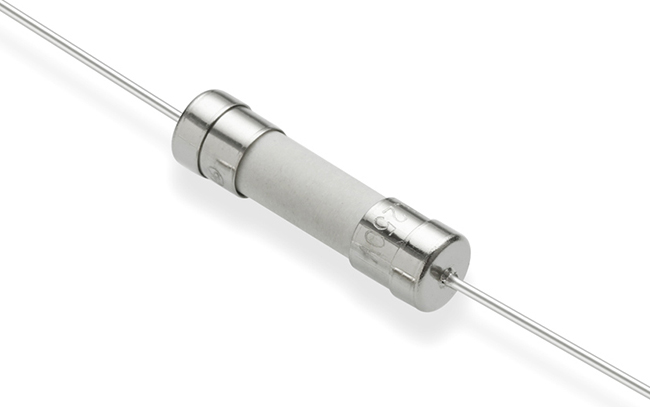
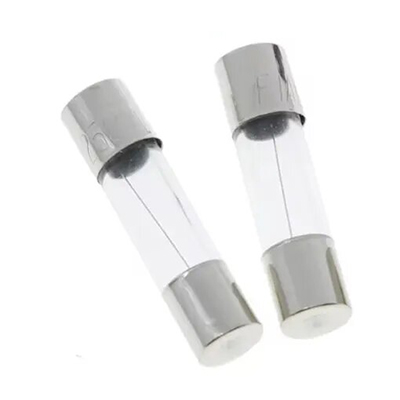
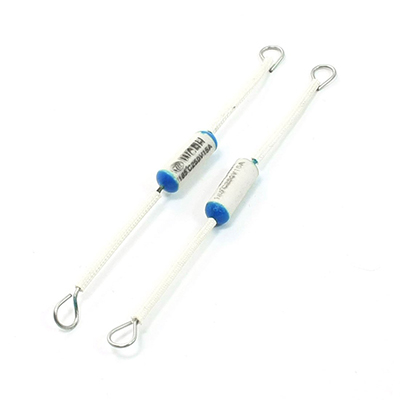
A thermal fuse, also known as a thermal cut-off, is a one-time-use safety device that protects electrical and electronic equipment from overheating. Unlike circuit breakers that can be reset, thermal fuses operate by using a heat-sensitive material (such as a fusible alloy or organic compound) that melts or decomposes when the ambient temperature reaches its rated value. Once activated, the thermal fuse breaks the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity and eliminating the risk of overheating-related failures, fires, or explosions. This makes thermal fuses essential for applications where continuous overheat protection is required, and resetting is not feasible or safe.
Key Application Fields of Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses are versatile components used across numerous fields due to their reliable overheat protection. In the electronics industry, they are integrated into power supplies, chargers, laptops, and audio equipment to prevent damage from component malfunctions that cause excessive heat. The automotive sector utilizes thermal fuses in battery management systems, engine control units, and in-car entertainment systems to ensure safety under high-temperature conditions. In household appliances, thermal fuses are a staple in microwaves, toasters, washing machines, and air conditioners, safeguarding users from potential fire risks. Additionally, they are widely used in industrial machinery such as motors, transformers, and heating equipment, as well as in renewable energy systems like solar inverters, where temperature fluctuations are common.
Thermal Fuse Application Industries
The demand for thermal fuses spans across multiple industries, each with specific requirements. The consumer electronics industry relies on compact, high-precision thermal fuses to fit into small devices while maintaining strict safety standards. The automotive manufacturing industry requires thermal fuses that can withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and humidity, making durability a key factor. Home appliance manufacturers prioritize cost-effective yet reliable thermal fuses to meet global safety certifications like UL, CE, and GS. The industrial sector, including heavy machinery and manufacturing plants, uses heavy-duty thermal fuses with high current ratings to protect large-scale equipment. Furthermore, the renewable energy industry is increasingly adopting thermal fuses to enhance the safety and longevity of solar and wind energy systems.
Thermal Fuse Product Models and Specification Parameters
Different application scenarios require thermal fuses with varying specifications. Below is a table of common thermal fuse models and their key parameters to help you select the right product:
| Model Number | Temperature Rating (°C) | Current Rating (A) | Voltage Rating (V AC/DC) | Package Type | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF-100 | 100 | 10 | 250V AC | Axial Lead | Microwaves, Toasters |
| TF-120 | 120 | 15 | 250V AC/32V DC | Radial Lead | Automotive Battery Management |
| TF-150 | 150 | 20 | 480V AC | Cartridge | Industrial Motors, Transformers |
| TF-85 | 85 | 5 | 125V AC/24V DC | Surface Mount | Laptops, Chargers |
| TF-200 | 200 | 25 | 600V AC | High-Temp Ceramic | Renewable Energy Inverters |
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Thermal Fuse
Selecting the appropriate thermal fuse requires considering several key factors. First, the temperature rating must match the maximum safe temperature of the equipment it is protecting—choosing a rating too high may fail to trigger protection, while one too low may cause false activation. Second, the current and voltage ratings should align with the circuit’s electrical parameters to ensure the fuse can handle normal operating conditions without tripping. The package type is also important, as it needs to fit the installation space and environmental conditions (e.g., surface mount for compact electronics, high-temp ceramic for industrial use). Additionally, ensuring compliance with industry certifications (UL, CE, RoHS) is crucial for meeting safety standards and market access requirements.