Battery Box Design That Endures Engine Bay Heat, Vibration, and Harsh Duty Cycles
News 2025-11-17
Battery boxes used in modern vehicles must perform far beyond simple mechanical protection. Located in crowded engine bays next to high-output powertrains, they face continuous thermal cycling, aggressive vibration spectra, road splash, and chemical exposure. A well-engineered enclosure preserves battery capacity, prevents premature failure, and stabilizes electrical performance for start-stop systems, safety electronics, and on-board diagnostics. For OEMs and aftermarket integrators, sturdy construction of the battery box is a key factor in meeting durability targets and warranty expectations.
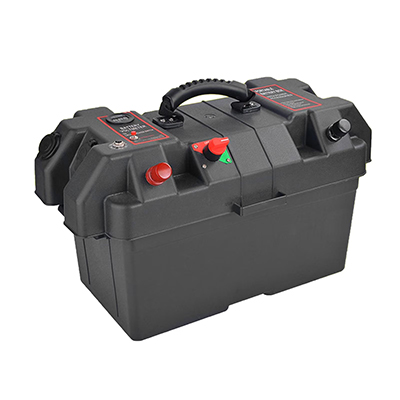

Engine Bay Operating Conditions
Battery enclosures operate in a thermally stressed environment where temperatures can swing from sub-zero cold starts to over 120°C near turbochargers and exhaust components. These conditions accelerate plate corrosion, electrolyte loss, and casing fatigue when the battery is poorly protected. A robust box uses heat-resistant polymers or coated steel, reinforced corners, and vented architecture to control hot spots while allowing safe gas dissipation. In off-road and commercial vehicles, shock loads from potholes, gravel roads, and heavy braking demand rigid mounting points, anti-loosening fasteners, and impact-dampening features that prevent the battery from shifting, cracking, or damaging terminals.
Structural Design and Material Selection
Mechanical strength starts with a rigid housing that resists deformation under clamping and vibration. High-temperature plastics such as glass-filled polypropylene or engineered nylon alloys combine dimensional stability with low weight, supporting easy installation in tight engine bays. Corrosion-resistant steel or aluminum boxes suit high-load, high-mass applications and can integrate welded brackets for direct chassis mounting. Internal bracing, ribbing, and reinforced lid structures keep the enclosure square, preserving consistent compression on the battery and minimizing micro-movement that can loosen posts and connectors. Chemical resistance to battery acid, oils, and road salt extends service life and reduces maintenance for fleet operators.
Vibration Management and Thermal Performance
Vibration is a primary cause of internal battery damage, from plate shedding to cracked welds. A sturdy box incorporates molded saddles, adjustable clamps, and elastomeric pads that isolate the battery from high-frequency engine vibration while maintaining secure restraint during severe maneuvers. Finite element analysis and shaker-table validation help match enclosure stiffness to vehicle-specific vibration profiles. Thermal performance is enhanced with strategic venting, optional heat shields near exhaust components, and integration with airflow paths inside the engine bay. In cold climates, the box can be paired with insulation or electric heating elements to support stable cranking performance and protect sensitive lithium chemistries.
Application Scenarios and Integration Benefits
In passenger cars, a compact, high-strength battery box supports start-stop systems and growing electrical loads from infotainment and ADAS modules. Light commercial vehicles and delivery fleets benefit from enclosures that withstand frequent cycling, extended idling, and constant vibration from urban routes. Heavy-duty trucks, agricultural machinery, and construction equipment require oversized boxes that accommodate higher-capacity batteries and resist damage from dust, mud, and high-pressure washing. For EV and hybrid platforms, battery auxiliary units in the engine bay or front compartment demand stringent containment for thermal events and must integrate seamlessly with harness routing, fusing, and diagnostic connectors. A strong enclosure simplifies assembly, reduces noise and rattles, and helps OEMs comply with safety and EMC standards.
FAQs on Engine Bay Battery Boxes
1. How does a sturdy battery box extend battery life?
A reinforced enclosure limits vibration, controls thermal exposure, and prevents mechanical shock, all of which reduce internal plate damage and terminal fatigue, helping the battery maintain capacity over a longer service interval.
2. Which materials are best for high-temperature engine bay battery boxes?
High-temperature polymers with glass reinforcement and corrosion-protected steel are commonly used, as they retain mechanical strength near engine heat sources while resisting chemicals, moisture, and road contaminants.
3. Why is vibration isolation inside the battery box important?
Vibration isolation prevents continuous mechanical stress on the battery plates and welds, reducing the risk of internal short circuits, cracked casings, and performance loss in demanding on-road and off-road applications.