Battery Box Secure Latches Enhance Safety and Stability for Automotive Power Systems
News 2025-11-17
In modern vehicles, battery box secure latches play a decisive role in keeping high-capacity automotive batteries firmly in place under harsh operating conditions. From compact passenger cars to heavy-duty trucks and off-road machinery, these latching systems protect the battery from vibration, impact, and accidental displacement. They also help maintain electrical integrity, prevent cable strain, and reduce the risk of short circuits caused by loose or shifting energy storage modules.
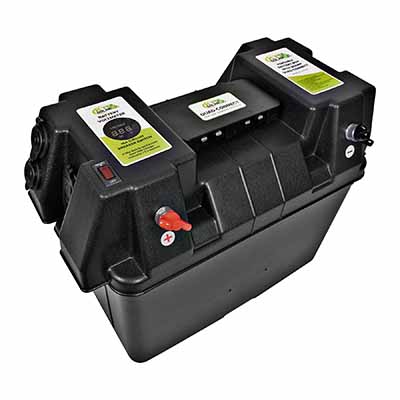

Key Functions of Secure Battery Box Latches
Secure latches provide mechanical retention for lead-acid, AGM, EFB, and lithium-based batteries housed in plastic or metal enclosures. Designed to withstand constant vibration and thermal cycling, they lock the battery box lid or frame to the vehicle structure so the battery cannot move during acceleration, cornering, or emergency braking. High-strength metals or reinforced polymers are applied to achieve stable clamping force, while ergonomic locking mechanisms allow technicians to open and reclose the box quickly during maintenance without sacrificing holding performance.
Automotive Application Scenarios and Environmental Demands
Battery box secure latches are widely deployed in engine compartments, under-seat battery trays, trunk-mounted auxiliary battery packs, and external chassis-mounted enclosures on commercial vehicles. In each location, the latch must resist exposure to road debris, water spray, salt, fuel mist, and temperature extremes. Off-road and construction vehicles demand even higher shock resistance and corrosion protection as they frequently encounter uneven terrain and continuous vibration. Electric vehicles and hybrids use multi-module battery assemblies, where a larger number of latches maintain alignment of the housing, safeguard high-voltage connections, and support rigorous crash and durability standards.
Performance Advantages and Design Features
High-performance latches deliver consistent clamping force over the vehicle lifetime, reducing the chance of fatigue loosening. Many designs integrate adjustable tension, positive tactile feedback, and secondary locking features that prevent accidental release. Corrosion-resistant coatings, sealed hinge points, and thermal-stable materials preserve functionality in hot engine bays and cold climates. Optimized geometry distributes loads evenly across the battery case, avoiding stress concentration that could damage the enclosure. For OEMs and system integrators, standardized latch interfaces simplify battery box design, shorten development time, and support modular platforms with varying battery sizes.
Installation, Maintenance, and Safety Considerations
Correct installation of battery box secure latches is vital for both electrical and mechanical safety. Mounting surfaces must be rigid and flat, and torque requirements for fasteners must be followed to ensure full locking engagement. During inspection, technicians should check for signs of corrosion, deformation, or play in the latch mechanism and verify that the lid closes flush with uniform pressure on the battery. Damaged or weakened latches must be replaced promptly to prevent battery movement that can lead to cracked terminals, insulation wear, or leakage. Well-engineered latching systems support compliance with automotive safety regulations and help fleet operators reduce unplanned downtime caused by battery-related failures.
1. Why are secure latches important for automotive batteries?
They stop the battery from shifting during vehicle operation, protect electrical connections, and reduce the risk of short circuits or mechanical damage.
2. Where are battery box latches typically used in vehicles?
They are commonly installed in engine bays, under-seat battery trays, trunk compartments, and chassis-mounted enclosures on commercial and off-road vehicles.
3. What characteristics define a high-quality battery box latch?
Key attributes include strong clamping force, corrosion resistance, durable materials, secondary locking features, and consistent performance under vibration and temperature extremes.