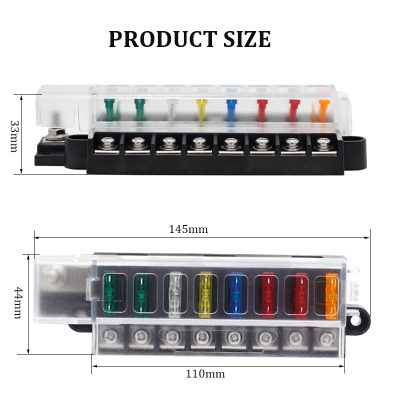
Damage Causes Affecting Fuse Box Integrity Beyond Electrical Overload Risks
News 2025-12-22
Fuse boxes operating in vehicles, industrial cabinets, or building distribution boards face a wide spectrum of threats that are not limited to electrical overload. Understanding these non-overload damage mechanisms helps engineers, maintenance teams, and facility managers select robust enclosures, improve system uptime, and protect downstream circuitry. Well-designed fuse boxes not only host protective components but also serve as a barrier against mechanical, environmental, and chemical stress in demanding application scenarios.

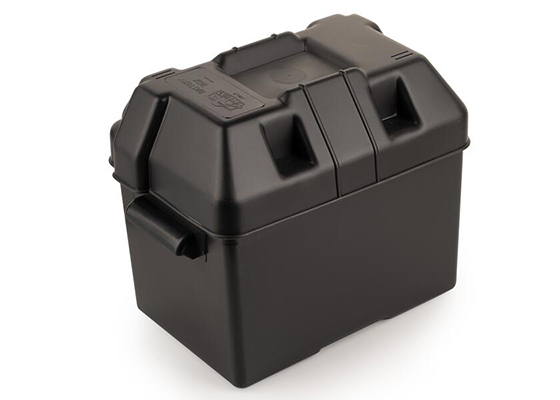
Mechanical Stress And Vibration-Induced Damage
Mechanical impact, shock, and continuous vibration can crack housings, loosen terminals, and deform busbars inside a fuse box. In automotive and rail applications, long-term exposure to road vibration and chassis flex can create micro-movements at connection points, increasing contact resistance and local heating without an actual overload event. Poor mounting, missing grommets, or incorrect torque of fasteners accelerates wear. Using vibration-rated fuse holders, reinforced plastic housings, and secure cable routing significantly improves mechanical performance and extends service life in mobile and industrial machinery platforms.
Moisture, Contaminants, And Corrosion Mechanisms
Ingress of moisture, dust, and corrosive gases often causes more fuse box failures than overcurrent events. In outdoor power distribution units, HVAC systems, and marine installations, condensation triggers oxidation of copper and tin surfaces, leading to green corrosion products and intermittent faults. Pollutants such as salt spray or industrial chemicals aggressively attack metal parts and screw clamps. Selecting enclosures with suitable IP ratings, employing conformal coatings, using corrosion-resistant alloys, and integrating breathable membranes or desiccants helps maintain stable contact resistance and long-term insulation performance in harsh environments.
Thermal Cycling, UV Exposure, And Material Aging
Repeated thermal cycling from ambient changes and normal load operation stresses plastic and elastomer materials in the fuse box assembly. In rooftop solar combiner boxes and outdoor telecom cabinets, continuous sun exposure causes UV-induced embrittlement, discoloration, and microcracking of the enclosure. These defects allow moisture ingress and reduce mechanical impact strength, even when currents remain within rating. Specifying UV-stabilized polymers, flame-retardant materials, and enclosures rated for extended temperature ranges enhances durability. Adequate ventilation paths and spacing also limit localized hot spots around high-current fuses and busbars.
Installation Errors And Improper Maintenance Practices
Incorrect wiring, undersized conductors, and loosely tightened terminals damage fuse boxes without any formal overload condition. Stranded conductors that are not fully inserted, or mixed metals without proper lugs, cause galvanic effects and concentrated heating. In commercial lighting panels and control cabinets, debris, metal shavings, or misaligned covers can short terminals or compromise creepage distances. Regular inspection, re-torque of terminal screws, thermal imaging checks, and replacement of aged components improve safety and reduce unplanned downtime, especially in mission-critical process control and data center environments.
Design Choices That Improve Fuse Box Robustness
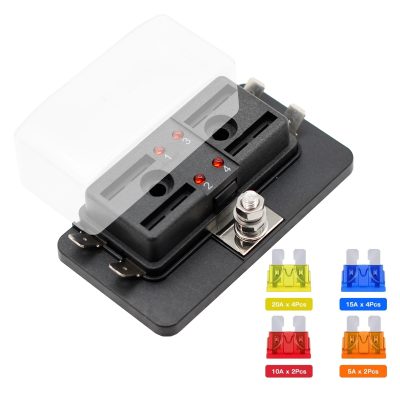
Well-engineered fuse boxes incorporate high-performance plastics, robust contact geometry, and clear labeling to minimize damage risks unrelated to overload. Features such as finger-safe terminals, integrated strain relief, touch-proof covers, and modular fuse carrier designs enhance serviceability in compact control panels, EV charging posts, and industrial drives. When combined with appropriate surge protection, cable management, and environmental sealing, modern fuse boxes deliver superior reliability, easier troubleshooting, and lower lifecycle cost.
1What causes fuse box failure in dry but dusty environments?
Dust accumulates on terminals and insulation surfaces, creating leakage paths and localized heating that degrade contacts and may lead to arcing, even when current remains within specification.
2How does vibration impact fuse box performance in vehicles?
Continuous vibration loosens screw terminals and connectors, increasing contact resistance, temperature rise, and the likelihood of intermittent power loss or premature fuse aging.
3Which design features improve outdoor fuse box durability?
Outdoor-ready fuse boxes benefit from UV-stable enclosures, high IP sealing, corrosion-resistant metals, and pressure equalization devices that limit condensation and moisture intrusion.