Heat Resistant Material Auto Fuse Enabling Stable Protection In High Temperature Vehicle Environments
News 2025-12-08
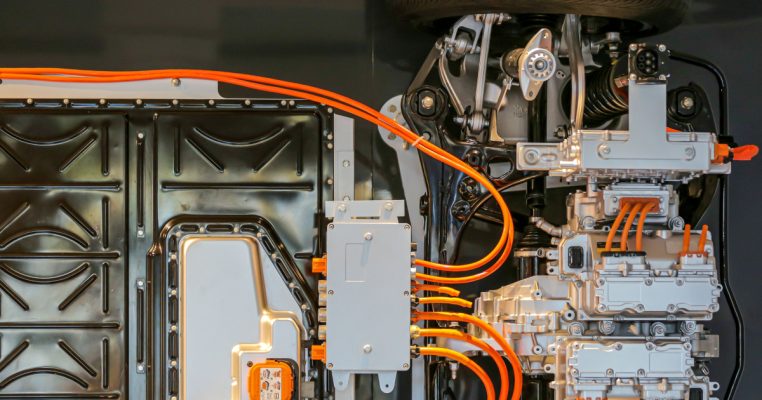
High temperature under‑hood zones and compact EV powertrains place extreme thermal stress on overcurrent protection components. A heat resistant material auto fuse is engineered to maintain stable electrical performance at elevated ambient temperatures where standard fuses degrade, drift in rating, or suffer premature aging. By combining temperature‑tolerant polymers, ceramic bodies, and high‑melting alloy elements, these fuses safeguard wiring harnesses, DC/DC converters, and battery circuits in demanding automotive conditions.

High Temperature Vehicle Application Scenarios
Heat resistant material auto fuses are widely used in engine compartments, turbocharged powertrains, start‑stop systems, and hybrid and battery electric vehicle architectures. Under these conditions, continuous ambient temperatures of 125–150°C are common, sometimes peaking higher near exhaust routing, inverters, or fast‑charging interfaces. Fuses must withstand thermal cycling, vibration, and exposure to fluids such as engine oil, brake fluid, and coolant. Typical applications include main power distribution boxes, PTC heaters, electric compressors, battery junction boxes, e‑axles, and on‑board chargers. Stable fuse behavior in these locations is vital to prevent nuisance blows during hot soak or high‑load operation, while still reacting quickly under true overcurrent or short‑circuit events.
Performance Advantages And Material Characteristics
The key advantage of heat resistant material auto fuses lies in their controlled fusing characteristics at high temperature. The fuse element is formulated to maintain predictable I²t and time‑current curves across a wide thermal range, minimizing derating in hot environments. High‑temperature plastics or ceramics used in the body offer elevated glass‑transition temperatures, low creep, and excellent arc resistance, helping preserve mechanical integrity under continuous heat and vibration. Terminals are often plated copper alloys that resist oxidation and ensure low contact resistance over the fuse lifetime. These material choices reduce the risk of thermal deformation, contact loosening, and long‑term drift, providing consistent protection performance that aligns with stringent automotive safety and EMC standards.
Design Considerations, Selection And Integration
When engineers select a heat resistant auto fuse, they must consider continuous current, ambient temperature, derating curves, and expected fault profiles. Correct sizing means using manufacturer data for high‑temperature operation instead of room‑temperature nominal values. Designers also evaluate voltage rating, breaking capacity, packaging style, and mounting position inside power distribution centers or near heat sources. PCB‑mount, bolt‑down, and plug‑in blade versions are available to match different harness and module designs. Thermal modeling of the fuse location, airflow conditions, and proximity to hot components helps prevent overheating beyond the specified limit. Compliance with ISO, SAE, and OEM test specifications, including thermal shock and vibration profiles, ensures long life in harsh vehicle environments.
Typical Use Cases And Reliability Benefits
In passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and construction equipment, heat resistant material auto fuses enable slimmer packaging and higher power density without sacrificing safety. For example, EV battery packs and high‑voltage junction boxes often operate in confined spaces where self‑heating and limited cooling raise internal temperature. Robust fuses in these locations support consistent short‑circuit protection over the vehicle lifetime, even under frequent fast charging and high current peaks. In trucks and buses, under‑hood fuse boxes see long idling times and severe thermal cycling; heat resistant fuses contribute to reduced maintenance, fewer unexpected trips, and better uptime. By ensuring accurate operation at rated current in hot conditions, these devices help OEMs meet warranty targets and regulatory safety requirements.
1, What temperature range can heat resistant auto fuses typically endure?
They generally support continuous operation around 125–150°C, depending on series and manufacturer, while still maintaining defined time‑current performance.
2, How do these fuses improve safety in electric vehicles?
They provide stable overcurrent protection in hot battery, inverter, and charging environments, lowering the risk of thermal runaway or wiring damage under fault conditions.
3, What factors should engineers check when choosing a heat resistant auto fuse?
Key factors include rated current and voltage, derating at high temperature, breaking capacity, mounting style, applicable automotive standards, and validation data under real vehicle thermal profiles.