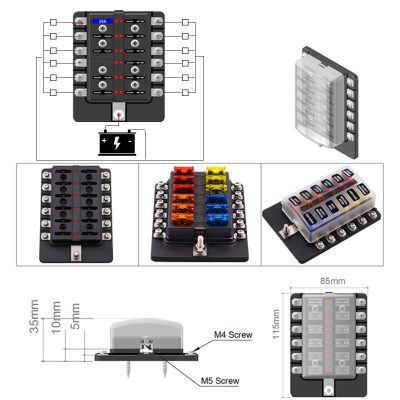
High-beam fuse protects high-beam headlight circuits from overloads and failures
News 2025-11-17
Automotive high-beam systems operate under demanding electrical and thermal conditions, especially in modern vehicles where halogen, HID, and LED technologies coexist. Within this environment, the high-beam fuse plays a decisive role in maintaining circuit integrity, preventing wiring damage, and safeguarding lighting modules during overcurrent events. By interrupting abnormal current flow before it reaches critical components, the fuse preserves the performance of high-beam headlights and supports road safety under night-time and adverse-weather driving.

Function and Working Principle of the High-Beam Fuse
The high-beam fuse is an overcurrent protection component inserted in series between the vehicle battery, switching device, and high-beam lamp load. When the operating current remains within the rated range, the fuse element maintains low resistance and negligible voltage drop. During short circuits, wiring faults, or internal defects in the headlamp module, the current rises sharply and heats the fusible link. Once the thermal energy exceeds the design threshold, the fuse element melts and opens the circuit, preventing excessive I²t stress on harnesses, switches, and semiconductors. Proper coordination between fuse rating, wire gauge, and high-beam current ensures selective protection, avoiding nuisance blowing while guaranteeing rapid response to genuine faults.
Application Scenarios in Modern Lighting Architectures
In traditional halogen systems, a blade-type high-beam fuse in the engine compartment fuse box protects both left and right lamps or separate channels per side, depending on the harness topology. In LED and matrix headlight platforms, high-beam fuses protect not only the LED arrays but also the DC-DC converters and driver ICs powering adaptive lighting functions. High-beam fuses are widely used in passenger cars, commercial trucks, buses, motorcycles, and off-road equipment, where long-duration high-beam usage and vibration demand robust protection. They also play a key role in retrofitted auxiliary driving lights, rally lamps, and agricultural lighting bars, where additional harnesses and high-power loads increase the risk of overcurrent and require dedicated fused circuits.
Performance Advantages and Selection Considerations
The performance of a high-beam fuse depends on its interrupt rating, time-current characteristic, temperature derating, and mechanical reliability. High-quality fuses offer stable operation under wide ambient temperatures, strong resistance to engine-compartment vibration, and consistent blowing behavior over the vehicle lifetime. Fast-acting types provide quick disconnection under short-circuit conditions, protecting delicate LED drivers and CAN-controlled modules, while medium-blow characteristics can tolerate brief inrush currents typical of halogen or HID ignition. Correct selection involves matching the fuse rating to the continuous lamp current, adding a safety margin for thermal aging, and verifying compliance with OEM and ISO standards. Optimized fuse dimensioning reduces unplanned service events, supports long headlamp life, and minimizes the risk of harness overheating that could lead to costly repairs.
Integration, Maintenance, and Safety Impact
Manufacturers typically place the high-beam fuse in a centralized fuse and relay box, enabling quick diagnostics and field replacement. Clear labeling, standardized blade profiles, and color coding simplify service procedures in workshops and roadside environments. For vehicle owners, a correctly functioning high-beam fuse means consistent light output, reduced probability of sudden lighting loss due to wiring damage, and compliance with regulatory requirements on headlamp performance. From a safety perspective, the fuse forms part of a coordinated protection strategy alongside relays, solid-state switches, and electronic control units. Optimized fuse design supports stable high-beam operation under continuous duty, frequent switching, and exposure to moisture and contaminants, contributing to better visibility and reduced accident risk during night driving.
1. What causes a high-beam fuse to blow?
Short circuits in the wiring harness, internal lamp failures, or incorrect aftermarket installations often drive current above the rated value, causing the fuse element to melt and open the circuit.
2. How should the correct high-beam fuse rating be chosen?
The rating should exceed the normal operating current of the high-beam circuit while accounting for inrush and ambient temperature, yet remain low enough to interrupt faults before wire insulation or modules are damaged.
3. Can an upgraded high-wattage bulb use the original fuse?
High-wattage bulbs typically draw more current than the OEM design, so keeping the original fuse may cause frequent blowing or unsafe heating; a complete evaluation of wiring, relays, and fuse sizing is required before any upgrade.