Fuse Tap: Efficient Circuit Extension Solution for Multiple Scenarios
Introduction
A fuse tap is a practical circuit expansion accessory designed to add auxiliary devices to existing fuse boxes without modifying the original wiring. Widely used in automotive electronics, marine systems, and household electrical setups, fuse taps enable safe, tool-free installation of accessories like dash cams, LED lights, and GPS devices. With different plug types and current ratings, fuse taps ensure compatibility with various fuse boxes while maintaining circuit protection, making them essential for DIY enthusiasts and professional installers alike.
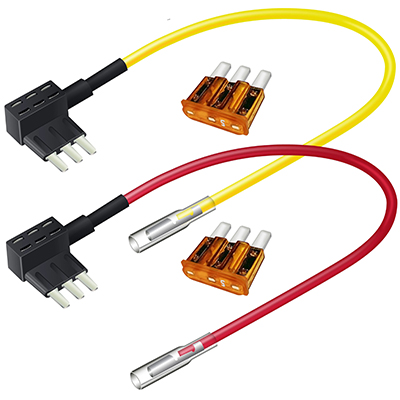

What is a Fuse Tap and How Does It Work?
A fuse tap, also known as a fuse adapter or add-a-circuit, is a small device that plugs into an existing fuse slot in a fuse box, creating an additional circuit for auxiliary devices. It features two fuse holders: one for the original circuit’s fuse (to maintain the original protection) and another for the new accessory’s fuse (to protect the added device). When installed, the fuse tap draws power from the vehicle or appliance’s electrical system through the existing fuse slot, eliminating the need for cutting or splicing wires. This plug-and-play design ensures a secure connection, prevents wiring damage, and allows for easy removal if the accessory is no longer needed.
Main Application Fields of Fuse Taps
Fuse taps are primarily used in fields requiring convenient circuit expansion without permanent modifications. In the automotive field, they are the go-to solution for installing dash cams, parking sensors, LED light bars, car chargers, and GPS trackers—common accessories that need a dedicated power source. The marine field utilizes fuse taps in boats and yachts to add electronics like fish finders, navigation lights, and radio systems, as they withstand damp environments. In household electrical setups, fuse taps are used for low-power accessories such as smart home sensors, small LED lighting, and portable appliances, especially in older homes with limited fuse box slots. Additionally, they find applications in RVs and campers for powering camping lights, refrigerators, and other on-the-go devices.
Industries Utilizing Fuse Taps
The demand for fuse taps spans industries focused on convenient and safe circuit modification. The automotive aftermarket industry is the largest user, as fuse taps are essential for installing aftermarket electronics in cars, trucks, and motorcycles—complying with automotive standards like SAE J1284. Marine electronics manufacturers recommend fuse taps for boat accessory installations, ensuring compliance with marine safety standards (ABYC). The DIY electronics and home improvement industry relies on fuse taps for user-friendly circuit expansion, with products meeting UL and CE certifications for household use. RV and camper manufacturers integrate fuse taps into their electrical systems to allow owners to add custom accessories easily. Furthermore, the professional installation industry (auto shops, marine service centers) uses fuse taps to provide efficient, non-destructive accessory installation for clients.
Fuse Tap Product Models and Specification Parameters
Different fuse box types and accessories require fuse taps with specific specifications. Below is a table of common fuse tap models and their key parameters to aid selection:
| Model Number | Fuse Type Compatibility | Max Current Rating (A) | Wire Gauge | Voltage Rating (V DC) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT-BLADE-M | Mini Blade Fuse | 15 | 16 AWG | 12-24 | Car Dash Cams, GPS |
| FT-BLADE-STD | Standard Blade Fuse | 20 | 14 AWG | 12-24 | LED Light Bars, Car Chargers |
| FT-BLADE-MAXI | Maxi Blade Fuse | 30 | 12 AWG | 12-24 | RV Refrigerators, Marine Fish Finders |
| FT-GLASS-5×20 | 5x20mm Glass Fuse | 10 | 18 AWG | 12-120 | Household Smart Sensors, Small LED Lights |
| FT-ATM-LP | LP Mini Blade Fuse | 7.5 | 18 AWG | 12-24 | Motorcycle Accessories, Parking Sensors |
Key Considerations When Choosing Fuse Taps
Selecting the right fuse tap requires evaluating several critical factors. Fuse type compatibility is paramount—ensure the tap matches the fuse size in your fuse box (e.g., mini blade, standard blade, glass). Max current rating must exceed the auxiliary device’s operating current to avoid overheating; for example, a 10A device needs a fuse tap rated for at least 10A. Wire gauge correlates with current capacity: thicker wires (lower AWG numbers) handle higher currents. Voltage rating should match the system voltage (12V for cars, 24V for trucks). Additionally, check for safety features like insulated housings and corrosion-resistant contacts, and ensure compliance with industry certifications (UL, SAE) for reliable performance. Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions to maintain circuit safety.


