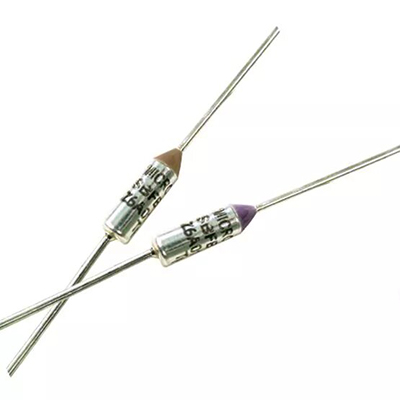
Robust Construction Quality Thermal Fuse Ensures Stable Protection In Harsh Conditions
News 2025-11-27
Robust-Construction-Quality Thermal Fuse Withstands Demanding Use
Rugged Construction for Harsh Electrical Environments
A robust-construction-quality thermal fuse is engineered to interrupt current once a defined temperature threshold is reached, protecting transformers, battery packs, heating elements, LED drivers, and power adapters from thermal runaway. Its design centers on a carefully calibrated fusible alloy, advanced organic or inorganic insulation, and a rigid encapsulation that resists vibration, dust, moisture, and mechanical stress. These structural elements allow the fuse to maintain predictable opening temperature, even in compact power-dense assemblies. By preventing insulation breakdown or internal deformation, the rugged housing preserves alignment of the thermal pellet and spring mechanism, helping ensure consistent operation across the full service life.
Stable Performance, Tight Tolerance, and Safety Compliance
High-performance thermal fuses are defined by narrow operating tolerance, low leakage current, and secure long-term stability under continuous load. Precision manufacturing controls the fusing temperature within a tight window, a key requirement for designers who must coordinate derating curves, PCB layout, and enclosure ventilation. Low internal resistance minimizes self-heating, which protects temperature accuracy under heavy current flow. Many products meet UL, VDE, and IEC standards and carry agency approvals that streamline safety certification of finished equipment. This combination of structural robustness and standards compliance reduces the risk of nuisance tripping while still reacting rapidly during fault conditions such as blocked airflow, overload, or component failure.
Key Application Scenarios in Modern Electronics
Demanding applications place strict expectations on thermal protection components. In AC adapters, chargers, and open-frame power supplies, the fuse must endure repeated inrush events, elevated ambient temperatures, and tight clearances around high-frequency transformers. In household appliances, small-form-factor fuses safeguard motor windings, heating plates, and control boards exposed to daily on-off cycling and occasional misuse. Energy storage systems and e-mobility chargers require thermal fuses capable of managing high continuous current, strong vibration, and fluctuating climate conditions. LED lighting drivers, coffee machines, HVAC controls, and industrial tools all rely on compact, rugged fuses that prevent catastrophic overheating while supporting dense, cost-optimized layouts.
Performance Advantages Over Conventional Thermal Protection
Compared to conventional thermal protectors or resettable devices, a robustly built thermal fuse offers decisive, non-resetting interruption that eliminates the risk of repeated operation in a damaged or unstable state. Solid construction improves heat transfer from the protected component to the fusible element, shortening response time under abnormal temperature rise. Enhanced mechanical strength withstands soldering heat, automated assembly, and long-term vibration without cracking or shifting internal parts. Stable characteristics enable engineers to model thermal behavior accurately, improving system MTBF and supporting extended warranty targets. The result is higher product safety, fewer field failures, and lower service costs across consumer, commercial, and industrial platforms.
Design Integration and Selection Considerations
When specifying a robust thermal fuse, engineers evaluate rated current, opening temperature, maximum operating voltage, insulation strength, and mounting method. Axial-leaded types fit through-hole boards and transformer windings, while radial or surface-mount versions serve compact switch-mode supplies and smart modules. Proper placement near heat sources, combined with realistic thermal simulation, ensures the device senses true worst-case temperature. Designers often pair the fuse with temperature sensors, PTC thermistors, or electronic controllers to build layered protection. Careful selection of clearance, creepage distance, and conformal coating preserves safety margins in polluted or humid environments, particularly in outdoor equipment and industrial control cabinets.
1How does a robust thermal fuse improve product safety?
It provides single-action interruption at a defined temperature, preventing overheating, fire risk, and damage to transformers, batteries, and heating elements when ventilation is blocked or components fail.
2Where is this type of thermal fuse typically used?
It is widely applied in AC adapters, household appliances, LED drivers, battery packs, industrial tools, HVAC systems, and other electronics that operate in harsh or space-constrained environments.
3What factors should engineers consider when choosing a thermal fuse?
Key factors include opening temperature, rated current, voltage rating, certification marks, package style, and the thermal coupling between the fuse body and the heat-generating component.


